However, after cardiac injury such as myocardial infarction, pump failure or 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C pressure overload, the mRNA and protein expression of periostin were greatly elevated in the heart. Periostin showed close relationship with pressure overload induced maladaptive left ventricular hypertrophy, which was highly associated with endstage heart failure. In periostin knockout mice, cardiac healing after AMI was impaired and more cardiac ruptures were found. Smaller and less abundant collagen was also seen in periostin knockout mice, suggesting impaired collagen fibril formation in the lack of periostin gene. Periostin overexpressed mensechymal stem cells implantation into the myocardium after AMI led to significantly histological and functional improvement, including decreased infarct size, reduced apoptotic myocardial cells and increased micro vessel density, indicating a cardio-protective role of periostin combined with stem cell transplantation. Gene polymorphisms analysis in Chinese population showed that rs3829365 of the periostin gene was associated with susceptibility to, and severity of heart failure, suggesting a role of periostin in Forsythin disease prediction and severity assessment. Acute myocardial infarction patients showed decreased circulating level of periostin compared with control volunteers and periostin level was in negative correlation with patients’ cardiac function three months after AMI. All these studies demonstrated that periostin acted as an important factor in the process of extracellular matrix remodeling under cardiac adverse conditions such as damage and pressure overload. This study investigated the association of serum periostin level with cardiac function, coronary situation, biomarkers and clinical characteristics in acute myocardial infarction patients. The six month 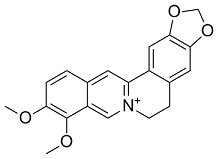 prognosis was also assessed. We found that serum periostin level was in negative association with left ventricular ejection fraction and left atrium diameter, in positive correlation with Killip class and showed no relationship with serum CK-MB or troponin T. Patients with higher serum periostin level exhibited increased composite cardiovascular events after six months follow up. In our study, serum periositn level showed negative correlation with LVEF, suggesting that patients with lower left systolic function had higher circulating periostin level. Killip class represented left ventricular failure degree in the acute period after AMI. Serum periositn level was in positive correlation with Killip class. This was in consistent with the results of periostin and LVEF, suggesting a relationship of higher periostin level with worse left ventricular function. CK-MB and troponin T are well documented serum biomarkers for myocardial infarction and reflected myocardium injury. We found no correlation between serum periositn and these two biomarkers, indicating that periositn was less likely an index related to myocardial injury. Whether higher circulating periostin level led to lower systolic function or resulted from worse heart function was not known. A lot of researches focused on the direct effect of periostin on cardiomyocytes and myocardium but had not reached a similar conclusion yet.
prognosis was also assessed. We found that serum periostin level was in negative association with left ventricular ejection fraction and left atrium diameter, in positive correlation with Killip class and showed no relationship with serum CK-MB or troponin T. Patients with higher serum periostin level exhibited increased composite cardiovascular events after six months follow up. In our study, serum periositn level showed negative correlation with LVEF, suggesting that patients with lower left systolic function had higher circulating periostin level. Killip class represented left ventricular failure degree in the acute period after AMI. Serum periositn level was in positive correlation with Killip class. This was in consistent with the results of periostin and LVEF, suggesting a relationship of higher periostin level with worse left ventricular function. CK-MB and troponin T are well documented serum biomarkers for myocardial infarction and reflected myocardium injury. We found no correlation between serum periositn and these two biomarkers, indicating that periositn was less likely an index related to myocardial injury. Whether higher circulating periostin level led to lower systolic function or resulted from worse heart function was not known. A lot of researches focused on the direct effect of periostin on cardiomyocytes and myocardium but had not reached a similar conclusion yet.