We, therefore, performed a case-control study of four SNPs located in the promoter, exonic, and intronic regions of EZH2 to assess the associations between these SNPs and HCC susceptibility and clinicopathologic characteristics. The major etiologies for HCC in Taiwan include infection with HBV or HCV, alcohol consumption, history of liver cirrhosis, and family history of HCC. In our HCC group, however, alcohol consumption and tobacco use were not significantly different from those of healthy controls, suggesting that these two risk factors alone do not fully explain the pathogenesis of HCC and that genetic components may play a pivotal role. This is consistent with the observations that many gene polymorphisms and somatic mutations have been associated with the preneoplastic stage of HCC. We observed that at least one polymorphic C allele at SNPs rs6950683 and rs3757441 is strongly associated with reduced HCC risk. Rs3757441 is an intronic SNP, and as such may affect gene expression through several mechanisms, including changes in transcription�Cfactor binding sites, microRNA-targeting sequences, and splicing variants. Rs6950683, is located upstream of exon 1, and, therefore, may impact gene expression by affecting promoter function. Further functional studies are AbMole Metaproterenol Sulfate needed to confirm the specific mechanisms by which these EZH2 polymorphisms influence the development of HCC. Although the functional importance of rs6950683 and rs3757441 has not been tested experimentally, it has been observed that individuals carrying C/C alleles at these two SNPs have a lower risk of lung cancer than do those carrying the T/T wild-type allele. This study provides novel information on the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms in EZH2 on HCC susceptibility and clinicopathology, but found that HCC patients carrying rs6950683 and rs3757441 polymorphisms have a higher risk of lymph node metastasis than wild-type carriers. However, the number of individuals examined in this study was relatively small, and additional studies with more patients are needed to verify the effects of EZH2 polymorphisms on HCC that we observed and to explore the effects of these variants on the biological function of EZH2. Although many SNPs have no direct effect on gene products, they can still be used as genetic markers to locate adjacent functional variants that contribute to disease. In addition, the contribution of SNPs to a disease-related haplotype may not be apparent when looking at individual SNPs. Therefore, haplotype analysis is sometimes advantageous over analysis of individual SNPs for detecting an association between alleles and a disease phenotype. Our haplotype analysis of the four EZH2 SNPs rs6950683, rs2302427, rs3757441, and rs41277434 revealed 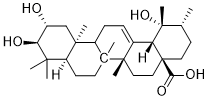 that the CCCA and CCTA haplotypes are associated with a lower risk of HCC. However, it is possible that these EZH2 SNPs are linked with other functional polymorphisms and are, therefore, not directly responsible for the decreased susceptibility to HCC. In conclusion, this is the first study to show a significant association between polymorphisms in EZH2 and HCC risk. These findings suggest that the presence of a variant EZH2 allele may be a protective factor for the development of HCC and could be a useful genetic marker for predicting susceptibility to HCC. Communication between nerve cells in the brain can simplistically be described as a biochemical concert of synaptic neurotransmitters, receptors, ion channels and effector molecules, coding and controlling signal AbMole (R)-(-)-Modafinic acid transmission. Regulation of signaling efficiency is basically controlled by down-stream regulating molecular system that modulates synaptic transmission.
that the CCCA and CCTA haplotypes are associated with a lower risk of HCC. However, it is possible that these EZH2 SNPs are linked with other functional polymorphisms and are, therefore, not directly responsible for the decreased susceptibility to HCC. In conclusion, this is the first study to show a significant association between polymorphisms in EZH2 and HCC risk. These findings suggest that the presence of a variant EZH2 allele may be a protective factor for the development of HCC and could be a useful genetic marker for predicting susceptibility to HCC. Communication between nerve cells in the brain can simplistically be described as a biochemical concert of synaptic neurotransmitters, receptors, ion channels and effector molecules, coding and controlling signal AbMole (R)-(-)-Modafinic acid transmission. Regulation of signaling efficiency is basically controlled by down-stream regulating molecular system that modulates synaptic transmission.
Month: March 2019
Another noteworthy finding with rapid and consistent reatment criteria in the BOLT
Studies were designed on the same principle of initiation phase followed by individualised PRN dosing schedule based on disease progression as judged by visual acuity and OCT changes, with a low threshold for re-treatment. In the RESTORE study, from month 3 to 11, monthly injections were given until vision was stabilised. Injections were re-initiated if there was BCVA decrease due to DMO progression. In DRCR.net study, re-injection was done in all visits in which there was an evidence of improvement. If success or failure criteria were met it was left to the investigator’s discretion to re-inject. The visual acuity eligibility criterion of the BOLT study was also different, with a lower visual acuity range of 35�C69 letters, unlike the DRCR.net study where 50% of the study eyes had $66 letters, and 19.8% of the RESTORE patients who a BCVA of more than 73 letters. Despite these aforementioned differences in baseline characteristics, the patterns of response of DMO to ranibizumab and bevacizumab are very similar when standard outcomes are assessed. But, this study also highlights important differences that should be explored in adequately powered larger studies. The median baseline CMT in the bevacizumab arm in the BOLT study for patients who exited at 24 months was higher than that of patients who completed 2 years in the DRCR.net trial, suggesting that comparisons between the drugs should be made with caution. However, whilst in the ranibizumab studies approximately 40% had persistent macular oedema defined as OCT central subfield $250 mm and only 20%�C24% had more than mildly thickened retina defined as OCT central subfield #250 mm at two years, the corresponding figures in the bevacizumab arm of the BOLT study were 65% and 56% respectively. This suggests that further studies should explore the concept that the ��drying effect’ of bevacizumab may be less effective than for Ranibizumab. Despite the fact that greater reductions in thickness were observed in BOLT participants with macular thickness of $400 mm compared to those with #400 mm, the mean 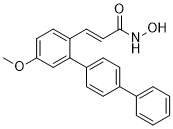 macular thickness was still $400 mm at 12 and 24 months, and the proportion that achieved a dry macula was limited to 14% and 27% at 12 and 24 months respectively. Similar effects were observed in the DRCR.net study. However, the proportion with $2 step log improvement in LogOCT was lower in the BOLT study compared to the DRCR.net study. Although the BOLT study is a small study, these exploratory analyses provide support for a comparative study of ranibizumab and bevacizumab. Some of these differences may be related to differences in molecular weight, half-life and degree of retinal penetration of bevacizumab and ranibizumab based on their structural differences. However, the importance of these proposed differences is controversial. Further studies are required to elicit the optimal therapeutic effect of bevacizumab in different retinal thickness profiles.
macular thickness was still $400 mm at 12 and 24 months, and the proportion that achieved a dry macula was limited to 14% and 27% at 12 and 24 months respectively. Similar effects were observed in the DRCR.net study. However, the proportion with $2 step log improvement in LogOCT was lower in the BOLT study compared to the DRCR.net study. Although the BOLT study is a small study, these exploratory analyses provide support for a comparative study of ranibizumab and bevacizumab. Some of these differences may be related to differences in molecular weight, half-life and degree of retinal penetration of bevacizumab and ranibizumab based on their structural differences. However, the importance of these proposed differences is controversial. Further studies are required to elicit the optimal therapeutic effect of bevacizumab in different retinal thickness profiles.
Feature of fast progression has brought great challenge for selecting the optimal time for starting therapy
In this study, two commonly used inoculation methods including VX2 cell suspension and VX2 tissue fragment were used to establish animal models. In our study, the tumor grew rapidly after implantation with a quick increase of the diameter and volume, leading to a shortened time span that was suitable for treatment. The animal model would have to be abandoned if the optimal intervention time was missed. The tumors derived from VX2 cell suspension and VX2 tissue fragment showed different growth behaviors. The tumors of the cell suspension group grew faster than those of the tissue fragment group. For animals inoculated using the tissue fragment method, the therapy starting point should be later than the one of animals inoculated using the cell suspension method. The rate of tumor visualization on CT scans on day 14 after implantation was low. On day 7, the visualization rate on plain and contrast-enhanced CT scans was 12.5% and 53.13%, respectively. CT scans did not reliably detect the tumors at very early period after implantation. The blood supply of human HCC comes from the portal vein at its very early stage. As the tumor grows the blood supply becomes progressively arterialized. The low visualization rate of CT scans may be due to the portal vein supply of the early-stage VX2 liver tumors or the improper enhanced phase used in CT enhanced scans. It is reported that the visualization rate of MRI scans was low at 1 week after implantation. the visualization rate of tumor on plain and contrast-enhanced MRI scans was 57.25% and 37.5%, respectively. Metastases and ascites were not observed on day 7 in both groups. On day 14, one case in the cell suspension group showed intra-hepatic and pulmonary metastases. We considered that the multiple metastases may be due to dissemination though blood vessels which were broken during VX2 cell suspension injection. This is also mentioned in previous literature. On day 21, metastases and ascites were observed in eight animals of the cell suspension group on CT scans. On day 28, most animals in the cell suspension group showed metastases and ascites. In the tissue fragment group, intra-hepatic metastases were only observed in one case on day 28. The average survival time of untreated animals was longer than 35 days. These results suggest that metastases and ascites might appear on approximately day 21 and 28, respectively in the cell suspension group and the tissue fragment group. Compared with the animals in the cell suspension group, the animals in the tissue fragment group indicated a longer survival time and a later occurrence of metastases and ascites. Three reasons may contribute to the difference. Firstly, the tumors in the cell suspension group grew 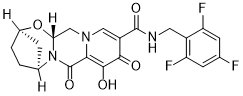 more fastly than those in the tissue fragment group, suggesting a more rapid disease progression; secondly, the way of tumor tissue implantation might influence its biological behavior.
more fastly than those in the tissue fragment group, suggesting a more rapid disease progression; secondly, the way of tumor tissue implantation might influence its biological behavior.
Short-term epidermal gene delivery is suitable for vaccination ulcer therapies and skin malignancy
Essential hypertension, defined as high blood pressure with no identifiable cause, affecting 95% of hypertensive patients. It is considered to be the consequence of an interaction between environmental and genetic factors. Hitherto, many candidate genes in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the sympathetic nervous system, and water-sodium balance system have been widely studied. Among all these genes which play important roles in the etiology of hypertension, those encoding the main components of the RAAS are deemed the most possible candidate genes since the RAAS plays a fundamental role in the maintenance of blood pressure and cardiovascular homeostasis. Epidermal gene transfer is suggested as a new therapeutic strategy for a variety of skin diseases, vaccination and systemic disorders. Long-term or persistent gene delivery to the epidermis has promise for inherited skin diseases and potentially systemic disorders. Topical application of plasmid DNA results in low levels and short duration of gene expression in epidermal skin. Cutaneous gene electrotransfer following intradermal DNA injection has been widely studied. The level and duration of gene expression is quite different, depending on which type of electrodes and which species of animals was utilized. However, definitive epidermal expression by GET in guinea pig or human skin xenograft mouse model has been demonstrated by only a few groups of researchers. The human skin xenograft mouse model may be the best choice for preclinical skin research. However, sources of human skin are very limited. A second option is hairless guinea 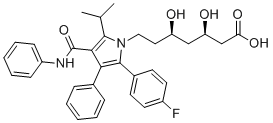 pig skin, whose skin is very similar to human skin anatomically and histologically as opposed to the skin of normal rodents. Previously, we demonstrated that GET to the skin resulted in efficient expression in rat and the Hartley guinea pig. In this study, we further characterize several important aspects associated with potential clinical applications, such as the level and duration of gene expression, distribution of gene expression within the tissue and side effects in this model. We also investigated if a therapeutic protein, human factor IX, could be expressed in the skin following delivery using the non-invasive MEA and whether it could reach the blood circulation. The xenograft human skin-SCID chimera has been reported as a valuable model for pathological research of several skin disorders including psoriasis, cutaneous lupus, pemphigus, vitiligo and androgenetic alopecia. However, the immune deficiency of the xenograft model limits its application for immunomodulation, including vaccination and immune therapy for skin cancer. A few skin electrotransfer studies have been performed in rabbit or pig skin, while most studies of skin GET have been performed in mouse or rat skin, which is significantly different from human skin.
pig skin, whose skin is very similar to human skin anatomically and histologically as opposed to the skin of normal rodents. Previously, we demonstrated that GET to the skin resulted in efficient expression in rat and the Hartley guinea pig. In this study, we further characterize several important aspects associated with potential clinical applications, such as the level and duration of gene expression, distribution of gene expression within the tissue and side effects in this model. We also investigated if a therapeutic protein, human factor IX, could be expressed in the skin following delivery using the non-invasive MEA and whether it could reach the blood circulation. The xenograft human skin-SCID chimera has been reported as a valuable model for pathological research of several skin disorders including psoriasis, cutaneous lupus, pemphigus, vitiligo and androgenetic alopecia. However, the immune deficiency of the xenograft model limits its application for immunomodulation, including vaccination and immune therapy for skin cancer. A few skin electrotransfer studies have been performed in rabbit or pig skin, while most studies of skin GET have been performed in mouse or rat skin, which is significantly different from human skin.
Some of these results demonstrate that evodiamine exhibits inhibitory effects on the growth
We performed a comparative assessment of the proposed methods on four different AbMole Gambogic-acid drug-target interaction networks from humans involving enzymes, ion channels, GPCRs and nuclear receptors. Results indicated that WNN is competitive in predicting interaction for unknown drug compounds with more involved machine learning methods recently proposed, notably a fully probabilistic method based on a Bayesian formulation that combines kernel-based nonlinear dimensionality reduction, matrix factorization and binary classification. Furthermore we showed that the direct integration of WNN in a recent kernel based machine learning method provides a general and powerful tool for finding drug-target interactions. A limitation of our approach is that it does not make a difference between an inactive target and a target that has not been measured for a compound. Compounds with a higher mutual chemical similarity also have a higher chance of having the same bioactivity. This information could be considered by WNN by determining directly the weights from the similarity, instead of using the proposed ranking-based decay mechanism. In this way all the compounds with high similarity would be considered with a high weight and all the compounds with low similarity would only have a minor contribution to the final predicted profile. On the same reasoning there is also a similarity threshold from where the chance is so low that two compounds have the same profile that it would be better not to predict something in the first place. In particular for new screening data from very large  screening libraries chances are high that none of the references are really similar to the screening hits, which would most likely have a detrimental effect in the overall prediction performance, if predictions would be made for all such compounds. Many published target prediction algorithms apply such “applicability domain” or confidence estimations for their predictions. WNN could be modified to address this issue for instance by including a binary annotation based on a similarity threshold, or a more advanced procedure based on the similarities of all compounds considered for the generation of the profile. The discovery and subsequent development of novel chemical entities into anti-cancer drugs are one of the major goals of oncologists. Compounds from traditional Chinese medicine have been examined for their anti-cancer potential in recent decades, and for those compounds that do exhibit such potential, the delineation of their mechanism of action may have an enormous influence on the development of new strategies in cancer therapies. Evodiamine is one of the important components of Chinese herb Wu-Chu-Yu. Numerous reports have revealed the effects of evodiamine including anti-angiogenesis, anti-tumor growth, anti-invasive and metastatic activities, up-regulating apoptosis anti-allergic effects, and anti-inflammatory effects.
screening libraries chances are high that none of the references are really similar to the screening hits, which would most likely have a detrimental effect in the overall prediction performance, if predictions would be made for all such compounds. Many published target prediction algorithms apply such “applicability domain” or confidence estimations for their predictions. WNN could be modified to address this issue for instance by including a binary annotation based on a similarity threshold, or a more advanced procedure based on the similarities of all compounds considered for the generation of the profile. The discovery and subsequent development of novel chemical entities into anti-cancer drugs are one of the major goals of oncologists. Compounds from traditional Chinese medicine have been examined for their anti-cancer potential in recent decades, and for those compounds that do exhibit such potential, the delineation of their mechanism of action may have an enormous influence on the development of new strategies in cancer therapies. Evodiamine is one of the important components of Chinese herb Wu-Chu-Yu. Numerous reports have revealed the effects of evodiamine including anti-angiogenesis, anti-tumor growth, anti-invasive and metastatic activities, up-regulating apoptosis anti-allergic effects, and anti-inflammatory effects.