Although there were very few reports regarding whether a cross-reaction exists between silkworm moth and mites, intra- and interspecies cross-reactivities among allergens from mites and cockroaches have been widely recognized. A previous immunochemical study has reported cross-reactivity existing between house dust mites and snails, crustaceans, cockroaches, chironomids, and other mite allergens. In the majority of related studies, house dust mite extracts proved to be a powerful inhibitor for the cross-inhibition tests, suggesting that it is the main Isoacteoside source of many allergens resulting in 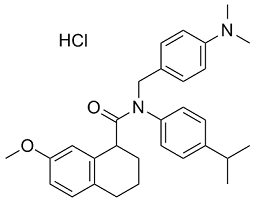 hypersensitivity. Our findings provide serum sIgE data showing that silkworm moth is an important allergen for respiratory allergies in the region and a positive correlation exists between silkworm moth and the relevant mites and cockroaches. We acknowledge that owing to the retrospective nature of the study, we cannot conclude on the cross-reaction between these allergens. Further serum inhibition studies are warranted to verify such relationship, and if so, it would be worthwhile to find out whether it is a ributed to arginine kinase. Features of Ursolic-acid diabetic retinopathy are retinal microaneurysms, retinal hemorrhages, retinal edema, retinal vein dilatation, and lipid deposition in the deep retinal layers. Since leakage of lipids, erythrocytes and serum through a vessel wall depends on the pressure in the vessel, since the diameter of a vessel also depends on its internal pressure, and since capillary blood pressure is influenced by the pressure in the draining veins, we assumed that an increased retinal vein pressure is a factor associated with presence and severity diabetic retinopathy. The blood pressure in the central retinal vein inside of the eye is at least as high as the orbital cerebrospinal fluid pressure, since the central retinal vein passes, after leaving the eye, through the optic nerve and the orbital cerebrospinal fluid space. We therefore put forward the hypothesis that an increased CSFP is associated with diabetic retinopathy. This hypothesis would fit with the role of arterial hypertension as risk factor for diabetic retinopathy, since a higher arterial blood pressure is associated with a higher CSFP. To test the hypothesis, we conducted a study in which we estimated the CSFP and compared eyes with diabetic retinopathy and eyes without diabetic retinopathy. In previous studies, the correlation between CSFP and age, arterial blood pressure and body mass index was described and a formula allowed estimating the CSFP. We used this formula to assess the CSFP in the participants of our study. We chose a population-based study design to avoid a referral induced bias in the selection of study participants. For all study participants, an interview was performed with standardized questions on the level of education, quality of life, known major systemic diseases, and other parameters. Fasting blood samples were taken for measurement of blood lipids, glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin HbA1c. Body height and weight and the circumference of the waist and hip were measured. The blood pressure was measured with the participant si ing for at least 5 minutes.
hypersensitivity. Our findings provide serum sIgE data showing that silkworm moth is an important allergen for respiratory allergies in the region and a positive correlation exists between silkworm moth and the relevant mites and cockroaches. We acknowledge that owing to the retrospective nature of the study, we cannot conclude on the cross-reaction between these allergens. Further serum inhibition studies are warranted to verify such relationship, and if so, it would be worthwhile to find out whether it is a ributed to arginine kinase. Features of Ursolic-acid diabetic retinopathy are retinal microaneurysms, retinal hemorrhages, retinal edema, retinal vein dilatation, and lipid deposition in the deep retinal layers. Since leakage of lipids, erythrocytes and serum through a vessel wall depends on the pressure in the vessel, since the diameter of a vessel also depends on its internal pressure, and since capillary blood pressure is influenced by the pressure in the draining veins, we assumed that an increased retinal vein pressure is a factor associated with presence and severity diabetic retinopathy. The blood pressure in the central retinal vein inside of the eye is at least as high as the orbital cerebrospinal fluid pressure, since the central retinal vein passes, after leaving the eye, through the optic nerve and the orbital cerebrospinal fluid space. We therefore put forward the hypothesis that an increased CSFP is associated with diabetic retinopathy. This hypothesis would fit with the role of arterial hypertension as risk factor for diabetic retinopathy, since a higher arterial blood pressure is associated with a higher CSFP. To test the hypothesis, we conducted a study in which we estimated the CSFP and compared eyes with diabetic retinopathy and eyes without diabetic retinopathy. In previous studies, the correlation between CSFP and age, arterial blood pressure and body mass index was described and a formula allowed estimating the CSFP. We used this formula to assess the CSFP in the participants of our study. We chose a population-based study design to avoid a referral induced bias in the selection of study participants. For all study participants, an interview was performed with standardized questions on the level of education, quality of life, known major systemic diseases, and other parameters. Fasting blood samples were taken for measurement of blood lipids, glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin HbA1c. Body height and weight and the circumference of the waist and hip were measured. The blood pressure was measured with the participant si ing for at least 5 minutes.
Month: April 2019
Diffusion is severely impaired by fibrosis of the alveolar matrix or by inflammatory cell infiltration
On respiratory function testing, the degree of gas transfer reduction is reflected by the decrease in the diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide, which is also reduced in DM-IP. However, in patients with severe DM-A/SIP, accurate pulmonary function testing is impossible due to complications such as dyspnea and pneumomediastinum. Therefore, the PO2 is simple and prognostically useful. In the DM-A/SIP patients treated by early CSA/PDN combination therapy, ferritin $600 ng/ml and PO2 $45 Torr were independent prognostic factors, and all patients with both of these factors died. In these patients, the outcome could not be improved even by additional treatments such as IVCY and IVIG. Recently, mycophenolate mofetil and blood purification therapy have been reported to be effective in patients with refractory DM-A/SIP. In patients with a poor prognosis, immunosuppressant therapy such as IVCY and mycophenolate mofetil and blood purification therapy should be considered from the beginning of treatment in addition to early CSA/PDN combination therapy. The clinical course of DM-A/SIP is rapidly progressive and this biomarker may not reflect the disease activity in rapid course of interstitial pneumonia. This study was carried out retrospectively in a small number of patients. In addition, autoantibodies and lung high-resolution computed tomography findings were not evaluated in all enrolled patients or in a large number of patients. Prognostic factors associated with the disease must still be extracted by evaluating a larger number of patients. In mammalian organisms, Campesterol steroid hormones are indispensable for a normal development. Considering their action, these steroids are classified into three main groups. Mineralocorticoids, with aldosterone as the most important representative, regulate the salt household and hence the blood pressure. Cortisol belongs to the glucocorticoids and provides the organism with energy stimulating the gluconeogenesis. Finally, the sexual hormones, with androgens and estrogens, are fundamental for the 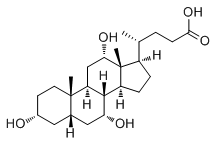 formation of the sexual characteristics and the estrous cycle. Biosynthesis of all steroid hormones is initiated by CYP11A1 with the side chain cleavage of cholesterol yielding pregnenolone. This ratelimiting step of the steroid hormone biosynthesis is carried out in the inner mitochondrial membrane and displays three hydroxylation reactions. In the first step, carbon C22 of cholesterol is hydroxylated followed by an oxidative attack at C20, forming the intermediate 20,22-dihdroxycholesterol. The cleavage of the side chain of cholesterol is initiated by a third hydroxylation. The electrons necessary oxygen activation and substrate hydroxylation are transferred from NADH via a NADH-depending 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C ferredoxin reductase, adrenodoxin reductase, and a ferredoxin, adrenodoxin. The product pregnenolone serves as precursor for mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, as well as DHEA and its derived sexual hormones. To induce their biological activities, according to recent hypothesis steroid hormones have to be available in an unconjugated form to interact with their corresponding receptors. Conjugated steroids with sulfate groups have been regarded for a long time to be exclusively designated for excretion.
formation of the sexual characteristics and the estrous cycle. Biosynthesis of all steroid hormones is initiated by CYP11A1 with the side chain cleavage of cholesterol yielding pregnenolone. This ratelimiting step of the steroid hormone biosynthesis is carried out in the inner mitochondrial membrane and displays three hydroxylation reactions. In the first step, carbon C22 of cholesterol is hydroxylated followed by an oxidative attack at C20, forming the intermediate 20,22-dihdroxycholesterol. The cleavage of the side chain of cholesterol is initiated by a third hydroxylation. The electrons necessary oxygen activation and substrate hydroxylation are transferred from NADH via a NADH-depending 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C ferredoxin reductase, adrenodoxin reductase, and a ferredoxin, adrenodoxin. The product pregnenolone serves as precursor for mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, as well as DHEA and its derived sexual hormones. To induce their biological activities, according to recent hypothesis steroid hormones have to be available in an unconjugated form to interact with their corresponding receptors. Conjugated steroids with sulfate groups have been regarded for a long time to be exclusively designated for excretion.
Enzymes found in nearly all organisms and they play a major role in the multidefence system
Two Sod enzymes have been identified in bacteria: a manganese Sod and an iron Sod, encoded by sodA and sodB, respectively. Oxidative stress is potentiated by iron because it reacts with H2O2 in the Fenton reaction. There is increasing evidence of the coordination between the regulation of iron homeostasis and the defences against oxidative stress. Remarkably, SodB is produced exclusively in high iron growth conditions. They can differentiate into mature, functional endothelial-like cells that can be incorporated into vessels and can Albaspidin-AA produce angiogenic factors that contribute to vascular repair and regeneration. Most studies focussed on the exploration of EPCs for therapeutic angiogenesis or the examination of EPCs as potential biomarkers for cardiovascular disease, have used cells that are generated by the culture of peripheral blood mononuclear cells on fibronectin in vascular endothelial growth factor -containing medium. These EPCs are not homogeneous but rather constitute a heterogenic population that mainly originates from myeloid hematopoietic cells. Furthermore, phenotypic analysis has revealed few EPCs expressing stem/progenitor-cell markers. These findings make it controversial to name these cells “EPCs” and the term “CACs” has been suggested, given that these cells have been shown to promote angiogenesis and vascular repair in various experimental settings. We hypothesized that CAC function from patients with HHT is impaired, and can be demonstrated in a series of in vitro cell function assays. ENG and ALK1 have been shown to be essential for the maintenance of endothelial cell morphology and structure. Fernandez et al. have shown that Isochlorogenic-acid-C circulating blood outgrowth endothelial cells derived from patients with HHT appear larger and rounder compared to the characteristic endothelial cobblestone shape of BOECs from control individuals. Furthermore, BOECs from individuals with HHT showed disorganization of the F-actin cytoskeleton, thought to be responsible for increased EC fragility and consequent capillary loss. Vessel injury in HHT patients occurs randomly as a result of inflammation, trauma and other adverse insults, and therefore rapid and efficient repair of the endothelium is critical. CACs contribute to vascular repair through transdifferentiation into ECs as well as through the production of angiogenic growth factors. We demonstrated in this study that CACs from HHT patients not only displayed a disparate morphology, but also had a reduced ability to differentiate to EC linage cells. In addition, mRNA levels of eNOS, an important angiogenic agent, were found to be significantly lower in CACs 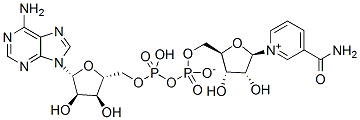 from HHT patients. Predictors of decreased eGFR after two years of ART included older age, lower BMI, and lower CD4 count but, notably, did not include the patient’s baseline eGFR or whether the patient received a tenofovir-containing regimen. In fact, our data showed a nonsignificant trend towards renal improvement in those who received tenofovir-containing regimens. Our findings support the WHO’s 2013 recommendation for a tenofovir-based first-line ART regimen and provide reassurance that, in most patients, tenofovir treatment likely does not require renal monitoring for toxicity.
from HHT patients. Predictors of decreased eGFR after two years of ART included older age, lower BMI, and lower CD4 count but, notably, did not include the patient’s baseline eGFR or whether the patient received a tenofovir-containing regimen. In fact, our data showed a nonsignificant trend towards renal improvement in those who received tenofovir-containing regimens. Our findings support the WHO’s 2013 recommendation for a tenofovir-based first-line ART regimen and provide reassurance that, in most patients, tenofovir treatment likely does not require renal monitoring for toxicity.
Some showed that periostin was able to induce cardiomyocytes proliferation in vitro and acted as a cardioprotective factor
However, after cardiac injury such as myocardial infarction, pump failure or 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C pressure overload, the mRNA and protein expression of periostin were greatly elevated in the heart. Periostin showed close relationship with pressure overload induced maladaptive left ventricular hypertrophy, which was highly associated with endstage heart failure. In periostin knockout mice, cardiac healing after AMI was impaired and more cardiac ruptures were found. Smaller and less abundant collagen was also seen in periostin knockout mice, suggesting impaired collagen fibril formation in the lack of periostin gene. Periostin overexpressed mensechymal stem cells implantation into the myocardium after AMI led to significantly histological and functional improvement, including decreased infarct size, reduced apoptotic myocardial cells and increased micro vessel density, indicating a cardio-protective role of periostin combined with stem cell transplantation. Gene polymorphisms analysis in Chinese population showed that rs3829365 of the periostin gene was associated with susceptibility to, and severity of heart failure, suggesting a role of periostin in Forsythin disease prediction and severity assessment. Acute myocardial infarction patients showed decreased circulating level of periostin compared with control volunteers and periostin level was in negative correlation with patients’ cardiac function three months after AMI. All these studies demonstrated that periostin acted as an important factor in the process of extracellular matrix remodeling under cardiac adverse conditions such as damage and pressure overload. This study investigated the association of serum periostin level with cardiac function, coronary situation, biomarkers and clinical characteristics in acute myocardial infarction patients. The six month 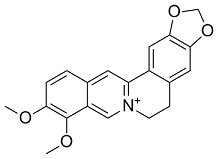 prognosis was also assessed. We found that serum periostin level was in negative association with left ventricular ejection fraction and left atrium diameter, in positive correlation with Killip class and showed no relationship with serum CK-MB or troponin T. Patients with higher serum periostin level exhibited increased composite cardiovascular events after six months follow up. In our study, serum periositn level showed negative correlation with LVEF, suggesting that patients with lower left systolic function had higher circulating periostin level. Killip class represented left ventricular failure degree in the acute period after AMI. Serum periositn level was in positive correlation with Killip class. This was in consistent with the results of periostin and LVEF, suggesting a relationship of higher periostin level with worse left ventricular function. CK-MB and troponin T are well documented serum biomarkers for myocardial infarction and reflected myocardium injury. We found no correlation between serum periositn and these two biomarkers, indicating that periositn was less likely an index related to myocardial injury. Whether higher circulating periostin level led to lower systolic function or resulted from worse heart function was not known. A lot of researches focused on the direct effect of periostin on cardiomyocytes and myocardium but had not reached a similar conclusion yet.
prognosis was also assessed. We found that serum periostin level was in negative association with left ventricular ejection fraction and left atrium diameter, in positive correlation with Killip class and showed no relationship with serum CK-MB or troponin T. Patients with higher serum periostin level exhibited increased composite cardiovascular events after six months follow up. In our study, serum periositn level showed negative correlation with LVEF, suggesting that patients with lower left systolic function had higher circulating periostin level. Killip class represented left ventricular failure degree in the acute period after AMI. Serum periositn level was in positive correlation with Killip class. This was in consistent with the results of periostin and LVEF, suggesting a relationship of higher periostin level with worse left ventricular function. CK-MB and troponin T are well documented serum biomarkers for myocardial infarction and reflected myocardium injury. We found no correlation between serum periositn and these two biomarkers, indicating that periositn was less likely an index related to myocardial injury. Whether higher circulating periostin level led to lower systolic function or resulted from worse heart function was not known. A lot of researches focused on the direct effect of periostin on cardiomyocytes and myocardium but had not reached a similar conclusion yet.
eNOS may be associated with a risk of developing idiopathic osteonecrosis
The reduction in the expression or activity of eNOS could result in lower production of NO and subsequent abnormalities in vascular reactivity, platelet recruitment, angiogenesis, bone  volume, and bone formation rate. It has been demonstrated that two polymorphic sites of the eNOS gene, the 27-bp repeat polymorphism in intron 4 and G894T polymorphism in exon 7, are Gentiopicrin associated with the altered function of this gene. A study in Korean patients demonstrated that polymorphism in intron 4 of eNOS was significantly associated with idiopathic femur head osteonecrosis, but the distribution of G894T polymorphisms was not significantly different between patients and controls. The T786C polymorphism is related to the G894T polymorphism and was also reported to be associated with eNOS gene function. Glueck et al. study in Caucasian and African American patients demonstrated that the T786C eNOS polymorphism and resultant reduction of nitric oxide production are associated with the pathogenesis of idiopathic ANFH. Although only a few studies investigated the association of eNOS polymorphism with the pathogenesis of ANFH, the effects of genetic differences between populations and confounders could not be excluded. Currently, no report has investigated the association between eNOS polymorphisms and pathogenesis of ANFH in Chinese patients. In this study, we investigated the 27-bp repeat polymorphism in intron 4 and G894T polymorphism in exon 7 of the eNOS gene in 125 Chinese patients with non-traumatic ANFH and evaluated ANFH according to the etiologic factors. Although non-traumatic ANFH has been widely recognized as a pathological state with multiple etiologies, the exact pathogenesis of Rosiridin osteonecrosis remains to be elucidated. Chronic steroid use and alcoholism were thought to be the main risk factors for osteonecrosis. Recent research has explored associations between genetic mutations, polymorphisms, and pathogenesis of ANFH. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the multidrug resistance gene have been revealed to be associated with corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis. Genetic variation of alcohol-metabolizing enzyme genes has been associated with alcoholism-induced osteonecrosis. Polymorphism in intron 4 and T786C polymorphism of eNOS were found to be significantly associated with idiopathic ANFH. In this study, we demonstrated that the frequency of 4a allele, b/a genotype in intron 4 and allele 894T, GT genotype in exon 7 were significantly higher in idiopathic subgroup of ANFH patients than in healthy controls. It has been demonstrated that the presence of 27-bp repeat polymorphism in intron 4 and G894T polymorphism in exon 7 could result in a change in eNOS expression and enzymatic activity. For example, plasma NO levels in subjects with the 4a allele of eNOS were significantly lower than those without the 4a allele. eNOS isoforms are processed differently within the cell depending on the presence of aspartate or glutamate at position 298 of the eNOS protein. Therefore, 4a and G894T gene polymorphisms can lead to low expression and activity of eNOS. Koo et al study in Korean patients demonstrated that the frequency of 4a allele and 4a/b genotype was significantly higher in femoral head osteonecrosis patients and idiopathic subgroup of FHON patients compared to healthy controls. In contrast, the distribution of G894T polymorphisms was not significantly associated with FHON. Consistent with the study in Korean patients, we observed that the frequency of 4a allele and 4a/b genotype was significantly higher in ANFH patients, especially in idiopathic osteonecrosis patients than in controls. In contrast, our study revealed that G894T polymorphism was significantly higher in ANFH patients as well as idiopathic osteonecrosis patients compared to controls.
volume, and bone formation rate. It has been demonstrated that two polymorphic sites of the eNOS gene, the 27-bp repeat polymorphism in intron 4 and G894T polymorphism in exon 7, are Gentiopicrin associated with the altered function of this gene. A study in Korean patients demonstrated that polymorphism in intron 4 of eNOS was significantly associated with idiopathic femur head osteonecrosis, but the distribution of G894T polymorphisms was not significantly different between patients and controls. The T786C polymorphism is related to the G894T polymorphism and was also reported to be associated with eNOS gene function. Glueck et al. study in Caucasian and African American patients demonstrated that the T786C eNOS polymorphism and resultant reduction of nitric oxide production are associated with the pathogenesis of idiopathic ANFH. Although only a few studies investigated the association of eNOS polymorphism with the pathogenesis of ANFH, the effects of genetic differences between populations and confounders could not be excluded. Currently, no report has investigated the association between eNOS polymorphisms and pathogenesis of ANFH in Chinese patients. In this study, we investigated the 27-bp repeat polymorphism in intron 4 and G894T polymorphism in exon 7 of the eNOS gene in 125 Chinese patients with non-traumatic ANFH and evaluated ANFH according to the etiologic factors. Although non-traumatic ANFH has been widely recognized as a pathological state with multiple etiologies, the exact pathogenesis of Rosiridin osteonecrosis remains to be elucidated. Chronic steroid use and alcoholism were thought to be the main risk factors for osteonecrosis. Recent research has explored associations between genetic mutations, polymorphisms, and pathogenesis of ANFH. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the multidrug resistance gene have been revealed to be associated with corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis. Genetic variation of alcohol-metabolizing enzyme genes has been associated with alcoholism-induced osteonecrosis. Polymorphism in intron 4 and T786C polymorphism of eNOS were found to be significantly associated with idiopathic ANFH. In this study, we demonstrated that the frequency of 4a allele, b/a genotype in intron 4 and allele 894T, GT genotype in exon 7 were significantly higher in idiopathic subgroup of ANFH patients than in healthy controls. It has been demonstrated that the presence of 27-bp repeat polymorphism in intron 4 and G894T polymorphism in exon 7 could result in a change in eNOS expression and enzymatic activity. For example, plasma NO levels in subjects with the 4a allele of eNOS were significantly lower than those without the 4a allele. eNOS isoforms are processed differently within the cell depending on the presence of aspartate or glutamate at position 298 of the eNOS protein. Therefore, 4a and G894T gene polymorphisms can lead to low expression and activity of eNOS. Koo et al study in Korean patients demonstrated that the frequency of 4a allele and 4a/b genotype was significantly higher in femoral head osteonecrosis patients and idiopathic subgroup of FHON patients compared to healthy controls. In contrast, the distribution of G894T polymorphisms was not significantly associated with FHON. Consistent with the study in Korean patients, we observed that the frequency of 4a allele and 4a/b genotype was significantly higher in ANFH patients, especially in idiopathic osteonecrosis patients than in controls. In contrast, our study revealed that G894T polymorphism was significantly higher in ANFH patients as well as idiopathic osteonecrosis patients compared to controls.