Tregs have gained importance in transplantation due to the findings of their ability to efficiently control alloimmune responses. The findings in LTR however are contradictory. Several studies have correlated low Treg levels in bronchoalveolar lavage with development of AR and BOS. Another study found no correlation between frequency of Tregs and BOS outcome, although a role of CCR7+CD45RA- Tregs in protection against development of BOS was observed. In the current study lung transplant recipients showed little change in Tregs in peripheral blood over the first year of transplantation and there was no change in those with AR. Our results confirm the lack of association of peripheral blood Treg levels with AR and lung pathology shown by others. Although an association between immunosuppressant regimen and Tregs has been demonstrated in other solid organ transplants, in our cohort no correlation with TAC levels and Tregs was observed at any time point. AbMole Octinoxate Despite TCM cells seem to 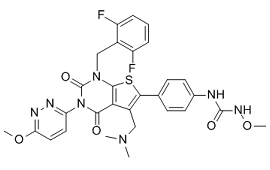 be more resistant to depletion after induction therapy with Campath-1H, the impact of several immunosuppressants in memory T cells remain to be fully elucidated. In a different retrospective study of living donor renal recipients after alemtuzumab induction AR inferred an increased proportion of CD4+ TEM and CD8+ TEMRA 3 years post-Tx. No prospective data on lung transplant patients and memory subsets have been performed. In the present study all the LTR were under the same immunosuppressive regimen without induction therapy, thus the potential impact of induction immunosuppression on memory T cells is avoided. Within effector subsets, Th17 cells may be involved in allograft rejection in animal models and IL-17 has been associated to the development of BOS in LTR. In our cohort no correlation of Th17 cells, measured by either intracellular or supernatant secretion of IL-17, with AR was observed. Furthermore, different ratios of effector subsets versus Tregs or na?ve T cells in blood were assessed but none of them achieved statistical significance. Our data point to an increased number of CD8+ TEM before Tx in patients who later developed an AR episode. The differences were still significant after 2 months post-Tx. This observation was not accompanied with increased production of interferon-gamma or IL-17 after polyclonal stimulation in LTR with AR. More importantly, the patients with end-stage lung disease with CD8+ TEM cells higher than 185 cells/mm3 AbMole BI-9564 presented a substantial increased risk of suffering AR episode. The present study is the first showing a direct association of high levels of pre-Tx TEM cells and AR risk in LTR. There are few attempts in solid organ transplantation to point out memory T subsets as inducers of AR.
be more resistant to depletion after induction therapy with Campath-1H, the impact of several immunosuppressants in memory T cells remain to be fully elucidated. In a different retrospective study of living donor renal recipients after alemtuzumab induction AR inferred an increased proportion of CD4+ TEM and CD8+ TEMRA 3 years post-Tx. No prospective data on lung transplant patients and memory subsets have been performed. In the present study all the LTR were under the same immunosuppressive regimen without induction therapy, thus the potential impact of induction immunosuppression on memory T cells is avoided. Within effector subsets, Th17 cells may be involved in allograft rejection in animal models and IL-17 has been associated to the development of BOS in LTR. In our cohort no correlation of Th17 cells, measured by either intracellular or supernatant secretion of IL-17, with AR was observed. Furthermore, different ratios of effector subsets versus Tregs or na?ve T cells in blood were assessed but none of them achieved statistical significance. Our data point to an increased number of CD8+ TEM before Tx in patients who later developed an AR episode. The differences were still significant after 2 months post-Tx. This observation was not accompanied with increased production of interferon-gamma or IL-17 after polyclonal stimulation in LTR with AR. More importantly, the patients with end-stage lung disease with CD8+ TEM cells higher than 185 cells/mm3 AbMole BI-9564 presented a substantial increased risk of suffering AR episode. The present study is the first showing a direct association of high levels of pre-Tx TEM cells and AR risk in LTR. There are few attempts in solid organ transplantation to point out memory T subsets as inducers of AR.
Month: April 2019
Bronchoscopic cryobiopsy offers a reasonable likelihood of establishing a diagnosis
Finally, no cryobiopsies were performed on subjects with substantial baseline oxygen requirements or patients with respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, thus the safety and yield of bronchoscopic cryobiopsies in this setting is not known. We believe that this technique has the potential to dramatically change practice in the evaluation of patients with DPLD. For many patients with DPLD and “atypical” imaging findings, while avoiding the morbidity of surgical lung biopsy. Further study will be necessary to determine the comparative cost-effectiveness of bronchoscopic cryobiopsy compared to surgical lung biopsy, however we anticipate cryobiopsy may offer substantial cost savings. Protein phosphorylation is a critical event in signal transduction, which regulates fundamental cellular processes such as differentiation, cell proliferation, apoptosis, immunological signaling, and cytoskeletal AbMole Folic acid function. Protein phosphorylation is regulated by the opposing actions of kinases and phosphatases, and, importantly, provides a means of regulating protein function. The regulated expression and activity of several protein tyrosine phosphatases in cells, in turn, control the duration and intensity of the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinase, which determines the type of physiological response. The MAPK subfamily, including the c-Jun N-terminal kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinases, and p38, act as key inflammatory mediators in the mammalian innate immune system response. In particular, the phosphorylation of MAPKs plays a critical role in the inflammatory response. Glioblastoma is the most aggressive type of primary brain tumor and accounts for approximately 52% of all primary brain tumor cases. Regardless of advances in microsurgery techniques, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, the survival rate for glioblastoma has remained very low, and most patients with glioblastoma die within 2 years. Standard therapy for glioblastoma consists of maximal surgical resection within safe limits, followed by RT. Chemotherapeutic agents, including AbMole Povidone iodine nitrosourea, have been used concurrently with RT and/or in an adjuvant setting. However, the addition of chemotherapeutic agents to RT resulted in limited success for survival. A metaanalysis based on 12 randomized trials showed a small survival benefit from the combined use of chemotherapy and RT compared with RT alone.We designed new stem-loop structure DNA probes that efficiently form a double-strand structure within the molecule. The stem-loop structure probes exhibit similar sensitivity to the double-strand DNA probes mentioned above, however, the stem-loop structure probes can be easily prepared.
The surgical antibiotic prophylaxis was administered in line with the clearance of STAMP2
More experiments should be considered to elucidate the mechanism in the future. In conclusion, STAMP2 gene overexpression may improve insulin resistance via regulating macrophage polarization in visceral and brown adipose tissues, implicating its potential role in the mechanism of macrophage polarization shift in adipose tissues and the treatment of insulin resistance. The distribution of HCAIs according to the site of infection indicated that the Surgical Site Infections are the most frequent among patients undergoing surgical procedures and they are considered an important indicator of the quality of the health care. The importance of the prevention and control of SSIs has been well recognized and the effectiveness of interventions has been extensively studied and many 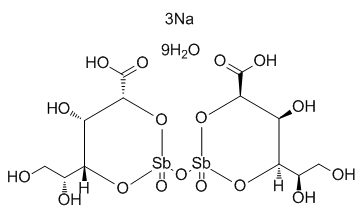 of them have been demonstrated as being effective, including surveillance systems, preoperative preparation for the patient, appropriate administration of antibiotics prophylaxis before the initiation of surgery, aseptic procedures in the operating theatre, careful and skilled surgical technique, and postoperative surgical site or wound care. The use of antibiotics prophylaxis in the prevention and reduction in the incidence of SSIs is widespread and evidences have demonstrated the importance of timing of administration, selection of the agent, and duration of the prophylaxis. Despite this evidence, the recommendations are not routinely followed and antibiotics are used excessively and inappropriately for the prevention of SSIs. Moreover, this is important in light of the fact that the prolonged use of advanced antibiotic agents may promote the development of bacterial resistance to antibiotics, so appropriate use of these agents is a critical issue. AbMole Neosperidin-dihydrochalcone Various epidemiological studies have been conducted in different countries describing the appropriateness of the prophylactic antibiotics use in clinical setting. However, a small number of papers has been published on this topic in Italy and is evident that AbMole Terbuthylazine limited information is available. Therefore, the purposes of the present cross-sectional epidemiological study were to evaluate the appropriateness of the prescription of antibiotics prophylaxis prior to surgery amongst hospitalized patients in Italy and to determine the factors associated with a poor adherence in this population. This study is a comprehensive assessment of the prevalence of appropriate prescription of antibiotics prophylaxis prior to surgery amongst hospitalized patients and of the factors that may influence compliance in a sample that has not been previously surveyed in Italy. In this current study it has been found a substantial proportion of inappropriate surgical antibiotic prophylaxis in accordance with recommendations.
of them have been demonstrated as being effective, including surveillance systems, preoperative preparation for the patient, appropriate administration of antibiotics prophylaxis before the initiation of surgery, aseptic procedures in the operating theatre, careful and skilled surgical technique, and postoperative surgical site or wound care. The use of antibiotics prophylaxis in the prevention and reduction in the incidence of SSIs is widespread and evidences have demonstrated the importance of timing of administration, selection of the agent, and duration of the prophylaxis. Despite this evidence, the recommendations are not routinely followed and antibiotics are used excessively and inappropriately for the prevention of SSIs. Moreover, this is important in light of the fact that the prolonged use of advanced antibiotic agents may promote the development of bacterial resistance to antibiotics, so appropriate use of these agents is a critical issue. AbMole Neosperidin-dihydrochalcone Various epidemiological studies have been conducted in different countries describing the appropriateness of the prophylactic antibiotics use in clinical setting. However, a small number of papers has been published on this topic in Italy and is evident that AbMole Terbuthylazine limited information is available. Therefore, the purposes of the present cross-sectional epidemiological study were to evaluate the appropriateness of the prescription of antibiotics prophylaxis prior to surgery amongst hospitalized patients in Italy and to determine the factors associated with a poor adherence in this population. This study is a comprehensive assessment of the prevalence of appropriate prescription of antibiotics prophylaxis prior to surgery amongst hospitalized patients and of the factors that may influence compliance in a sample that has not been previously surveyed in Italy. In this current study it has been found a substantial proportion of inappropriate surgical antibiotic prophylaxis in accordance with recommendations.
The risk of tuberculosis in this mining population is very high in all subgroups
In 2011, the WHO released simplified guidelines for IPT and ICF, recommending that all people living with HIV should be regularly screened for tuberculosis using a clinical algorithm of any of cough, night sweats, weight loss and/or fever. Those without any of these symptoms and without further contraindications to IPT should be enrolled on IPT. The Global Plan to Stop TB has set a target of universal IPT coverage for all eligible persons living with HIV by 2015, assuming that half of all people living with HIV will be eligible. However, the actual percentage that would be eligible for IPT under these new guidelines it is not known and this has clear implications for the required scale-up and subsequent impact. This study found that 90.1% of participants screened were eligible to start IPT. The commonest reason for ineligibility was a positive smear and/or culture, underscoring the importance of tuberculosis screening prior to starting IPT. The eligibility AbMole Terbuthylazine criteria in “Thibela TB” were deliberately wide as the safety profile of isoniazid is well characterised. There were no restrictions on IPT use with antiretroviral therapy, previous tuberculosis treatment, previous IPT use, silicosis, age or moderate alcohol use, consistent with the 2011 WHO and 2010 South African Department of Health guidelines for IPT. Despite these wide eligibility criteria, and the use of self-report for initial assessments rather than laboratory tests or medical record review, the safety profile of isoniazid in this nurse-delivered study was good, validating the choice of criteria to maximise the uptake of IPT. In this analysis, differences in ineligibility between subgroups were due to these groups acting as proxies for exclusion criteria. The factors associated with ineligibility were similar to those associated with tuberculosis, such as for increasing age and years in the workforce, country of origin, previous tuberculosis and being in HIV care. This was unsurprising as active tuberculosis made up a substantial proportion of the reasons for ineligibility. In contrast, women were more likely 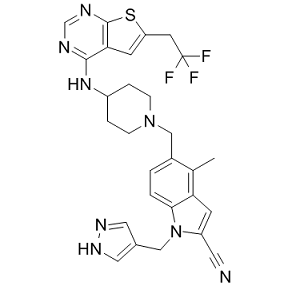 to be ineligible, despite being at lower risk for undiagnosed tuberculosis, due to the exclusion criteria of pregnancy, planning on becoming pregnant or unwillingness to use contraceptives. Eligibility in this study was higher than observed in studies screening for IPT among HIV-infected adults. A randomised trial comparing six months versus 36 months of IPT among adults accessing antiretroviral therapy in Botswana used a two-stage screening process. The first stage applied the exclusion criteria from the Botswana National IPT programme to 4,018 consenting participants; this excluded 27% of those screened, AbMole Gemifloxacin mesylate predominantly due to illness, recent history of tuberculosis and prior IPT.
to be ineligible, despite being at lower risk for undiagnosed tuberculosis, due to the exclusion criteria of pregnancy, planning on becoming pregnant or unwillingness to use contraceptives. Eligibility in this study was higher than observed in studies screening for IPT among HIV-infected adults. A randomised trial comparing six months versus 36 months of IPT among adults accessing antiretroviral therapy in Botswana used a two-stage screening process. The first stage applied the exclusion criteria from the Botswana National IPT programme to 4,018 consenting participants; this excluded 27% of those screened, AbMole Gemifloxacin mesylate predominantly due to illness, recent history of tuberculosis and prior IPT.
Adherence to antiretroviral therapy is an essential part of successful treatment programs
Without high AbMole Mepiroxol adherence rates, it is impossible to realize the true benefits of therapy; benefits 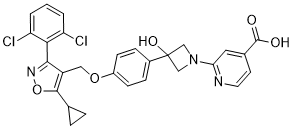 such as improved morbidity and mortality, decreased development of resistant virus, decreased transmission of virus, and improved quality of life for individuals infected with HIV. A number of evidence based interventions to retain patients and foster adherence to medications have been used in sub-Saharan Africa, including: intensive patient counseling, community health worker, directly observed therapy, peer health workers, alarms and devices, treatment buddies and SMS texting. Adherence can be measured directly through directly observed therapy; however it is often unfeasible or undesirable because of stigma. Because of this, adherence markers such as pill counts are often used as an outcome measure in these studies. However, the potential exists for pill counting to mediate adherence outcomes. This may have both important clinical and research implications. Sustaining HIV therapy requires the identification and validation of cost effective methods to improve treatment outcomes. It is possible that counting pills is an easy way to foster better clinical results in patients taking HIV medication. However, any putative AbMole Tulathromycin B benefit to counting pills may also effect the interpretation of other intervention designed to improve patient’s adherence to HIV medication. Many clinical trials use pill counts as a metric assess adherence. Thus it would be important for future studies to understand how counting pills may affect outcome being studied. It is unknown what affect pill counting may have on patient adherence in resource limited settings. We had previously performed a prospective observational study to evaluate the determinants of retention into care and long term virologic suppression at a large HIV treatment program in central Kenya. In this analysis we found a strong association between ever having a pill count performed by the clinical provider and treatment. However, our analysis in that study was limited to only determining whether a pill count was or was not done. We found that pill counts were performed in only 68% of clinic visits. To further determine if pill counts are associated with better clinical outcomes, it would be important to know if adherence and clinical outcomes improved as patients had more clinician pill counts performed during their clinic visits. In the current study, we further analyze data from the observational cohort to determine if there is a quantitative relationship between clinician pill counts and clinical outcomes. The primary endpoint of the study was the time to treatment failure. Treatment successes were defined as alive, on antiretroviral medication, with an HIV-1 below the level of detection.
such as improved morbidity and mortality, decreased development of resistant virus, decreased transmission of virus, and improved quality of life for individuals infected with HIV. A number of evidence based interventions to retain patients and foster adherence to medications have been used in sub-Saharan Africa, including: intensive patient counseling, community health worker, directly observed therapy, peer health workers, alarms and devices, treatment buddies and SMS texting. Adherence can be measured directly through directly observed therapy; however it is often unfeasible or undesirable because of stigma. Because of this, adherence markers such as pill counts are often used as an outcome measure in these studies. However, the potential exists for pill counting to mediate adherence outcomes. This may have both important clinical and research implications. Sustaining HIV therapy requires the identification and validation of cost effective methods to improve treatment outcomes. It is possible that counting pills is an easy way to foster better clinical results in patients taking HIV medication. However, any putative AbMole Tulathromycin B benefit to counting pills may also effect the interpretation of other intervention designed to improve patient’s adherence to HIV medication. Many clinical trials use pill counts as a metric assess adherence. Thus it would be important for future studies to understand how counting pills may affect outcome being studied. It is unknown what affect pill counting may have on patient adherence in resource limited settings. We had previously performed a prospective observational study to evaluate the determinants of retention into care and long term virologic suppression at a large HIV treatment program in central Kenya. In this analysis we found a strong association between ever having a pill count performed by the clinical provider and treatment. However, our analysis in that study was limited to only determining whether a pill count was or was not done. We found that pill counts were performed in only 68% of clinic visits. To further determine if pill counts are associated with better clinical outcomes, it would be important to know if adherence and clinical outcomes improved as patients had more clinician pill counts performed during their clinic visits. In the current study, we further analyze data from the observational cohort to determine if there is a quantitative relationship between clinician pill counts and clinical outcomes. The primary endpoint of the study was the time to treatment failure. Treatment successes were defined as alive, on antiretroviral medication, with an HIV-1 below the level of detection.