We found that LC couldenhance accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins indicative of proteasome inhibition;further enhance the decrease of CT-like activity induced by Vel;induce Bax accumulation at a posttranscriptional level. These results demonstrate that LC enhanced Vel-induced proteasome inhibition. How LC sensitizes Velinduced proteasome inhibition needs to be further investigated. Since LC as a HDAC inhibitor could induce multiple protein acetylations, this modification would affect protein degradation. On one hand, protein modification like acetylation would affect protein ubiquitination thus inhibiting protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system; On the other hand, the proteasome b5 subunit modification by acetylation could not be excluded. Proteasome inhibition has been well known to induce cell death via multiple mechanisms SB203580 in vivo including activating unfolded protein response. As WZ8040 expected, proteasome inhibition by Vel dose dependently induced UPR; the combination therapy enhanced this UPR and accordingly initiated caspase activation. We have reported that Bax accumulation plays an important role in proteasome inhibition-induced cell apoptosis, in the current study, it was confirmed 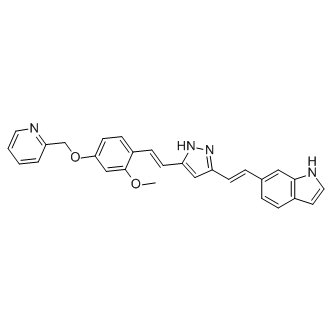 that Bax plays an important role in the combination-induced cell apoptosis. Even though we did not see much changes of all the HDAC gene expressioncontrary to previuos report, here we did find that Vel and LC combination increased histone acetylation especially in the animal tumor tissues. Like HDAC inhibitors, the accumulation of acetylated histones by either LC or Vel does not appear to be global. The GAPDH and p27kip1 genes are not transcriptionally activated, and there is no change in the level of acetylated histone in chromatin associated with these genes in response to LC or Vel. Even though it has been reported that Vel could increase p21cip1 expressionor histone acetylationrespectively, this is the first time to report that Vel increases p21cip1 expression associated with p21cip1 promoter gene-related histone acetylation. In this study, it looks like that Vel-induced histone acetylation is not associated with HDAC downregulation, contrary to the previous report, which need to be investigated in the future. These results confirmed that the combination of Vel and LC synergistically and selectively induced p21cip1 expression associated with the accumulation of acetylated histones in chromatin associated with the p21cip1 gene but not p27kip1, which possibly contributed to cell proliferation arrest. Vel has been approved by FDA to treat multiple myeloma malignanceand also tested under clinical trial in some solid tumors, and LC has been widely and safely used as heath supplement under many clinical conditions. Therefore, the synergistic effect of LC and Vel in cancer therapy will have great potential in the future clinical trials. The increasing rate of bacterial resistance against available antibacterial agents is becoming a serious threat to our society. Therefore, the development of new antimicrobial agents that act through new targets is an important task. Peptidoglycan is one of the main components of the bacterial cell wall, and it represents one of the most frequently used targets for antibacterial agents. However, the intracellular steps of peptidoglycan synthesis have been greatly under-exploited. Only two such antibacterial agents are in clinical use: fosfomycin and D-cycloserine. The Mur ligases are essential intracellular bacterial enzymes that are involved in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan precursors and thus represent attractive targets for the development of novel antibiotics.
that Bax plays an important role in the combination-induced cell apoptosis. Even though we did not see much changes of all the HDAC gene expressioncontrary to previuos report, here we did find that Vel and LC combination increased histone acetylation especially in the animal tumor tissues. Like HDAC inhibitors, the accumulation of acetylated histones by either LC or Vel does not appear to be global. The GAPDH and p27kip1 genes are not transcriptionally activated, and there is no change in the level of acetylated histone in chromatin associated with these genes in response to LC or Vel. Even though it has been reported that Vel could increase p21cip1 expressionor histone acetylationrespectively, this is the first time to report that Vel increases p21cip1 expression associated with p21cip1 promoter gene-related histone acetylation. In this study, it looks like that Vel-induced histone acetylation is not associated with HDAC downregulation, contrary to the previous report, which need to be investigated in the future. These results confirmed that the combination of Vel and LC synergistically and selectively induced p21cip1 expression associated with the accumulation of acetylated histones in chromatin associated with the p21cip1 gene but not p27kip1, which possibly contributed to cell proliferation arrest. Vel has been approved by FDA to treat multiple myeloma malignanceand also tested under clinical trial in some solid tumors, and LC has been widely and safely used as heath supplement under many clinical conditions. Therefore, the synergistic effect of LC and Vel in cancer therapy will have great potential in the future clinical trials. The increasing rate of bacterial resistance against available antibacterial agents is becoming a serious threat to our society. Therefore, the development of new antimicrobial agents that act through new targets is an important task. Peptidoglycan is one of the main components of the bacterial cell wall, and it represents one of the most frequently used targets for antibacterial agents. However, the intracellular steps of peptidoglycan synthesis have been greatly under-exploited. Only two such antibacterial agents are in clinical use: fosfomycin and D-cycloserine. The Mur ligases are essential intracellular bacterial enzymes that are involved in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan precursors and thus represent attractive targets for the development of novel antibiotics.