In conclusion, obtain tissue for histologic and gene expression measurements. TLR and interleukin activation, PPARc-inhibition and regulation of PRNP, occurs in both TNBS-colitis and IBD. TNBScolitis is an appropriate IBD-model to study specific biological processes like TNF signaling, Cell junction organization, and Interleukin-1 processing. We conclude that the TNBS-model may be suitable for studying agents targeting these pathways and provide translational information for clinical studies. Such high mortality rates are due to majority of patients presenting with advanced disease at the time of diagnosis. More than 90% of the patients have better prognosis if the Lomitapide Mesylate cancer is detected in its earliest stages. Treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer generally involves surgical debulking followed by chemotherapy with a combination of platinum and a taxane-containing agent. However, majority of patients recur and ultimately succumb to their cancer. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop new therapeutics that can be more effective in treating ovarian cancer and delaying or preventing recurrences. Novel therapies that target ovarian tumorigenesis are extensively been researched, but we have yet to come up with a promising drug.Nanotechnology based tools and techniques are rapidly emerging in the fields of medical imaging and targeted drug delivery. Cerium oxide is a rare-earth oxide that is found in the lanthanide series of the periodic table. Nanocrystalline cerium oxide exhibits a blue shift in the ultraviolet absorption spectrum, the shifting and broadening of Raman allowed modes and lattice expansion as compared to bulk cerium oxide indicating its unique properties. NCe has emerged as a lucrative material in biomedical science due to its unique ability to switch oxidation states Butenafine hydrochloride between and depending upon the environment. The ability to switch between mixed oxidation states of nanoceria is comparable to biological antioxidants. This imparts nanoceria with a very important biological property of radical scavenging which can be tuned based upon the retention of oxygen vacancies and concentration of Ce3+ species in nanoceria. The reversibility of oxidation state is the key property in making nanoceria a potent antioxidant, thereby reducing the need for frequent repeated dosage. Previous studies have demonstrated that 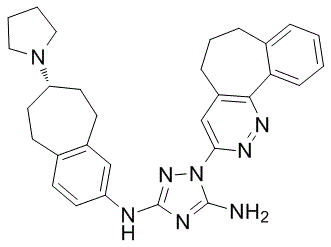 cerium oxide nanoparticles possess excellent antioxidant properties and act as potent, regenerative free radical scavengers in biological systems. These regenerative antioxidant properties are due, in part, to the valence structure of the cerium atom combined with inherent defects in the crystal lattice structure, which are magnified at the nano-scale. It has been suggested that the unique structure of engineered cerium oxide nanoparticles, with respect to valence and oxygen defects, promotes cell longevity and decreases toxic insults by virtue of its antioxidant effects that occur when the nanoparticles enter the cells, preventing the accumulation of reactive oxygen species in the cell. Tumor angiogenesis is characterized by the formation of new irregular blood vessels from a preexisting vascular network. This abnormal angiogenesis is required for the growth, survival, and metastasis of most solid tumors. Vascular endothelial growth factor is one of the most important pro-angiogenic factors, which acts as a mitogen for vascular endothelial cells in vitro and as an angiogenic factor in vivo. It is over expressed in various human cancers including OvCa.
cerium oxide nanoparticles possess excellent antioxidant properties and act as potent, regenerative free radical scavengers in biological systems. These regenerative antioxidant properties are due, in part, to the valence structure of the cerium atom combined with inherent defects in the crystal lattice structure, which are magnified at the nano-scale. It has been suggested that the unique structure of engineered cerium oxide nanoparticles, with respect to valence and oxygen defects, promotes cell longevity and decreases toxic insults by virtue of its antioxidant effects that occur when the nanoparticles enter the cells, preventing the accumulation of reactive oxygen species in the cell. Tumor angiogenesis is characterized by the formation of new irregular blood vessels from a preexisting vascular network. This abnormal angiogenesis is required for the growth, survival, and metastasis of most solid tumors. Vascular endothelial growth factor is one of the most important pro-angiogenic factors, which acts as a mitogen for vascular endothelial cells in vitro and as an angiogenic factor in vivo. It is over expressed in various human cancers including OvCa.
Category: clinically Small Molecule
Learned to use this non-recycling collagen uptake pathway for its own benefit a2b1 integrin cofractionates with detergent-resistant membranes
On the plasma membrane, a2b1 integrin colocalizes first with GPI-anchored proteins but is sorted out from GPIanchored proteins during internalization. However, later, the multivesicular bodies become increasingly positive for caveolin-1 suggesting that stable lipid microdomains exist in these endosomes. Interestingly, our previous intraendosomal pH measurements have shown that a2-MVBs are not acidic and do not associate with lysosomal structures. As these structures have proven to be important for viral uncoating and genome egress for replication, as well as for location of enhanced integrin turnover, the characterization and role 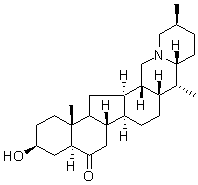 of the lipid microdomains is important to understand the structure and function of these novel non-acidic multivesicular bodies. Many Cinoxacin viruses, such as HIV, hepatitis C virus, West Nile virus, vaccinia virus and poliovirus depend on plasma membrane Gomisin-D cholesterol for efficient cell entry and replication. However, the putative role of these lipids in internalized endosomes has not been demonstrated. The cellular cholesterol concentration varies largely depending on the compartment membrane. Most of the cholesterol can be found at the plasma membrane, but also many intracellular organelles contain raft-like microdomains. In addition, studies on acidic late endosomes have revealed that raft-like membranes rich in cholesterol, sphingomyelin and raft proteins – can be found not only on the limiting membranes but also on the internal membranes of these multivesicular organelles. In late endosomes, cholesterol accumulation can lead to disturbed vesicle trafficking from the structures, underlining the importance of membrane cholesterol in these intracellular organelles. In this study, we investigated whether cholesterol plays a role in ligand uptake, virus uncoating in endosomes and the biogenesis of the non-acidic multivesicular bodies. We showed that the formation of a2-MVBs is highly dependent on cholesterol and that perturbation of cholesterol inhibits collagen and EV1 entry as well as virus uncoating and infection. Cholesterol depletion also decreased strong integrin and aerolysin labeling in the cell boundary and both labels were more scattered on the plasma membrane. Secondly, we labeled plasma membrane cholesterol by filipin staining. This labeling showed also less colocalization after ketoconazole treatment. In addition, a further treatment with cold Triton X-100 caused depletion of integrin labeling after ketoconazole treatment suggesting that integrin had moved out from the detergent-resistant domain to Triton X-100 soluble domain on the plasma membrane. a2 integrin distribution after ketoconazole treatment was further studied in detail with electron microscopy. The micrographs revealed that lipoprotein starved cells showed structures that were already partially multivesicular after 30 min internalization as we had observed before for normal biogenesis of a2-MVBs whereas in ketoconazole-treated cells integrin was found mainly on plasma membrane. After 3.5 h, lipoprotein-starved cells contained a2-MVBs with increasing amounts of intraluminal vesicles and internal membranes compared to 30 min time point as has been shown for a2 integrin internalization pathway previously. In contrast, no integrin containing multivesicular structures were observed in ketoconazole-treated cells, and the few found cytoplasmic structures showed tubular elements that are characteristic of the earliest forms of endosomes after integrin entry, suggesting that the biogenesis of multivesicular structures was halted.
of the lipid microdomains is important to understand the structure and function of these novel non-acidic multivesicular bodies. Many Cinoxacin viruses, such as HIV, hepatitis C virus, West Nile virus, vaccinia virus and poliovirus depend on plasma membrane Gomisin-D cholesterol for efficient cell entry and replication. However, the putative role of these lipids in internalized endosomes has not been demonstrated. The cellular cholesterol concentration varies largely depending on the compartment membrane. Most of the cholesterol can be found at the plasma membrane, but also many intracellular organelles contain raft-like microdomains. In addition, studies on acidic late endosomes have revealed that raft-like membranes rich in cholesterol, sphingomyelin and raft proteins – can be found not only on the limiting membranes but also on the internal membranes of these multivesicular organelles. In late endosomes, cholesterol accumulation can lead to disturbed vesicle trafficking from the structures, underlining the importance of membrane cholesterol in these intracellular organelles. In this study, we investigated whether cholesterol plays a role in ligand uptake, virus uncoating in endosomes and the biogenesis of the non-acidic multivesicular bodies. We showed that the formation of a2-MVBs is highly dependent on cholesterol and that perturbation of cholesterol inhibits collagen and EV1 entry as well as virus uncoating and infection. Cholesterol depletion also decreased strong integrin and aerolysin labeling in the cell boundary and both labels were more scattered on the plasma membrane. Secondly, we labeled plasma membrane cholesterol by filipin staining. This labeling showed also less colocalization after ketoconazole treatment. In addition, a further treatment with cold Triton X-100 caused depletion of integrin labeling after ketoconazole treatment suggesting that integrin had moved out from the detergent-resistant domain to Triton X-100 soluble domain on the plasma membrane. a2 integrin distribution after ketoconazole treatment was further studied in detail with electron microscopy. The micrographs revealed that lipoprotein starved cells showed structures that were already partially multivesicular after 30 min internalization as we had observed before for normal biogenesis of a2-MVBs whereas in ketoconazole-treated cells integrin was found mainly on plasma membrane. After 3.5 h, lipoprotein-starved cells contained a2-MVBs with increasing amounts of intraluminal vesicles and internal membranes compared to 30 min time point as has been shown for a2 integrin internalization pathway previously. In contrast, no integrin containing multivesicular structures were observed in ketoconazole-treated cells, and the few found cytoplasmic structures showed tubular elements that are characteristic of the earliest forms of endosomes after integrin entry, suggesting that the biogenesis of multivesicular structures was halted.
Further highlighting as stem cell self-renewal through controlling localization of Smad
TAZ plays an important role in the progression of breast and non-small cell lung cancer. Importantly, TAZ confers cancer stem cell-related traits on breast cancer cells, its importance in tumor initiation and progression. TAZ is also overexpressed in papillary thyroid carcinoma. TAZ and YAP have been shown to interact with several transcriptional factors, with the TEAD family of transcriptional factors being the most relevant in cell proliferation and cancer progression. The X-ray crystal structures of YAP-TEAD complexes have been resolved and the proposed interaction is supported by and consistent with functional analysis, showing that YAP-TEAD complexes activates gene transcription. YAP expression was observed in colon adenocarcinoma. It is overexpressed in human colon cancer specimens and overexpression of YAP promotes cell proliferation and survival in colon cancer cells. Recent findings show that knockdown of TAZ results in a decrease in cell proliferation in culture and tumor growth in vivo. Despite evidence suggesting the potential implication of YAP and TAZ in colon cancer progression, their prognostic significance in colorectal cancer is unknown. In this study, we analyzed the mRNA expression of YAP and TAZ, and two of its downstream target genes, AXL and CTGF, in two independent colon cancer patient cohorts comprising 522 patients. We found that TAZ, but not YAP, is a prognostic marker in colon cancer progression. Furthermore, TAZ-AXL-CTGF co-overexpression, which defines both the expression of TAZ and its transcriptional activity on target gene expression, is a novel prognostic indicator, that is independent of tumor grade and stage, for colon cancer patients. The role of TAZ in colon cancer cell proliferation and oncogenesis was validated by functional study. The top 20 small molecules were further analyzed Albaspidin-AA through a Pubmed search regarding their effects on treatment of colon cancer. We found that amiloride and tretinoin have yielded 55 and 123 publications, respectively, when coupled with colon cancer in the search engine. Several publications have shown their inhibitory effect on colon cancer growth. Amiloride treatment has been shown to inhibit the growth of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, it can sensitize 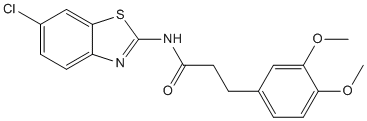 doxorubicin resistant colon cancer cells to treatment with doxorubicin, suggesting that amiloride and doxorubicin can be combined to treat doxorubicin resistant colon cancer. Tretinoin, also known as alltrans retinoic acid, has been shown to inhibit proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo, probably through regulating the differentiation state of cancer cells. In the present study, we have shown that TAZ mRNA expression is positively correlated with two of its downstream targets, AXL and CTGF, and that TAZ is significantly associated with poor survival of colon cancer patients in two independent colon cancer datasets, comprising 522 patients. Interestingly, the upregulation of AXL and CTGF, which reflects the increased transcriptional activity of TAZ-TEAD complexes, can be used in combination with TAZ mRNA expression, for better prognostification in these two independent colon cancer patient datasets. Genes that are co-regulated with TAZ-AXL-CTGF overexpression are involved in several important cellular processes, including cell migration, angiogenesis and calcium signaling, as well as others that have already been Pimozide described as prognostic markers for colon cancer progression. These genes may be upstream factors or downstream effectors of TAZ and the dysregulated Hippo pathway in colon cancers.
doxorubicin resistant colon cancer cells to treatment with doxorubicin, suggesting that amiloride and doxorubicin can be combined to treat doxorubicin resistant colon cancer. Tretinoin, also known as alltrans retinoic acid, has been shown to inhibit proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo, probably through regulating the differentiation state of cancer cells. In the present study, we have shown that TAZ mRNA expression is positively correlated with two of its downstream targets, AXL and CTGF, and that TAZ is significantly associated with poor survival of colon cancer patients in two independent colon cancer datasets, comprising 522 patients. Interestingly, the upregulation of AXL and CTGF, which reflects the increased transcriptional activity of TAZ-TEAD complexes, can be used in combination with TAZ mRNA expression, for better prognostification in these two independent colon cancer patient datasets. Genes that are co-regulated with TAZ-AXL-CTGF overexpression are involved in several important cellular processes, including cell migration, angiogenesis and calcium signaling, as well as others that have already been Pimozide described as prognostic markers for colon cancer progression. These genes may be upstream factors or downstream effectors of TAZ and the dysregulated Hippo pathway in colon cancers.
The MglA/SspA complex in the modulation of expression of pathogenicity genes during host invasion
A similar phenomenon was reported for inhibitors of the QseC membrane histidine kinase in Salmonella typhimurium and F. tularensis. The addition of LED209 did not influence the growth of Salmonella typhimurium in vitro, while it diminished the expression of virulence genes by 3-fold. This small decrease in the expression of the sifA pathogenicity gene, which is required for the establishment of S. typhimurium in the host, was sufficient to reduce bacterial counts in the liver and spleen of infected animals by 10-fold. Similarly, LED209 reduced the expression of FPI genes iglC and pdpA in F. tularensis by 3-fold in vitro, while clearing the infection in vivo. 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol quinacrine has been used as an antimalarial agent in humans, as an in vitro anti-prion agent, and as a neutralizing agent for Bacillus anthracis. While most research in these systems is oriented to isolate compounds with better affinities and lower host toxicity, Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate scarce information is available regarding the specific residues involved in such interactions. Quinacrine disrupts protein-protein interactions in the anti-apoptotic member Bcl-xl, by specifically binding in the hydrophobic grove, competing with the regulatory peptide BH3. As a desired result, apoptosis was induced in cancer cells. To determine the specific residues involved in the binding to quinacrine, a model of the tertiary structure of the MglA/SspA complex was built. Subsequently, site directed mutagenesis was performed in the heterodimer interface, where several residues were 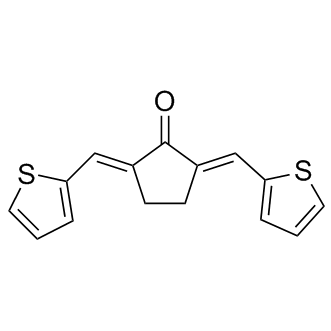 identified that affected the binding of quinacrine. Mutations to residues Y63 in Ft-MglA, and K97 in Ft-SspA had the greatest effect on the binding of quinacrine, as determined in the two-hybrid system. These results suggest the importance of these residues during interactions of the complex with quinacrine. However, the putative use of quinacrine as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of tularemia disease would require further chemical engineering to improve the affinity for the Ft-MglA/Ft-SspA complex. Recently, Mays et al. have used chemical synthesis to improve the antiprion activity of quinacrine derivatives that bind PrP with higher affinity. Based on the results obtained here, we propose the use of quinacrine as a chemical probe to uncover biologically relevant molecules that may modulate Ft-MglA/Ft-SspA activity, by binding in the heterodimer interface. In addition, it is also an important ingredient in the traditional medicine in treating wounds, headaches, indigestion and rheumatism. During the whole growth season from March to October, Sagittaria trifolia, like most wetland species, is grown in the shallow water, such as the pools, water gardens, tanks or tubs in the greenhouse, which indicates that the plant has developed mechanisms of surviving in the submerged environment. For the regeneration of this plant, bare root stocks or seedlings are directly planted into wetland soil. Several buds from the main stem develop into stolons, and the corms are formed at the tips of each stolon. Actually, corm, tuber, rhizome and bulbs are kinds of underground stems, and work as storage organs. These are storage units for food that provide the plants with the energy for growth, blooming, and completing their lifecycle. The process of corm formation can be classified into three stages: induction, initial swelling, and swelling stage. Stolon tips grow radially in the induction stage. In the second stages, longitudinal growth of stolon stops and its tips swell. At this swelling stage, great amounts of carbohydrates are synthesized in the storage.
identified that affected the binding of quinacrine. Mutations to residues Y63 in Ft-MglA, and K97 in Ft-SspA had the greatest effect on the binding of quinacrine, as determined in the two-hybrid system. These results suggest the importance of these residues during interactions of the complex with quinacrine. However, the putative use of quinacrine as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of tularemia disease would require further chemical engineering to improve the affinity for the Ft-MglA/Ft-SspA complex. Recently, Mays et al. have used chemical synthesis to improve the antiprion activity of quinacrine derivatives that bind PrP with higher affinity. Based on the results obtained here, we propose the use of quinacrine as a chemical probe to uncover biologically relevant molecules that may modulate Ft-MglA/Ft-SspA activity, by binding in the heterodimer interface. In addition, it is also an important ingredient in the traditional medicine in treating wounds, headaches, indigestion and rheumatism. During the whole growth season from March to October, Sagittaria trifolia, like most wetland species, is grown in the shallow water, such as the pools, water gardens, tanks or tubs in the greenhouse, which indicates that the plant has developed mechanisms of surviving in the submerged environment. For the regeneration of this plant, bare root stocks or seedlings are directly planted into wetland soil. Several buds from the main stem develop into stolons, and the corms are formed at the tips of each stolon. Actually, corm, tuber, rhizome and bulbs are kinds of underground stems, and work as storage organs. These are storage units for food that provide the plants with the energy for growth, blooming, and completing their lifecycle. The process of corm formation can be classified into three stages: induction, initial swelling, and swelling stage. Stolon tips grow radially in the induction stage. In the second stages, longitudinal growth of stolon stops and its tips swell. At this swelling stage, great amounts of carbohydrates are synthesized in the storage.
The number of Gomisin-D dendrites was counted dLGN projection Butenafine hydrochloride neurons have lost of their dendrites
During the next four days, massive cell death in the dLGN ensues, with many injured dLGN projection neurons displaying cytoplasmic vacuoles, disrupted membranes and nuclear condensation. Many trophic factors, such as nerve growth factor, fibroblast growth factor-2, brain-derived Orbifloxacin neurotrophic factor, ciliary neurotrophic factor and glial cellderived neurotrophic factor, have been demonstrated to mitigate the severity of neuronal loss after injury or disease. Some of these factors have been used to mitigate axotomyinduced cell death in the rat dLGN, and among them CNTF and FGF2 have been shown to be effective. A single administration of FGF2 at the time of axotomy increased the number of surviving dLGN neurons 3 months after axotomy up to 110% compared to controls. FGF2, a member of a family of proteins that bind heparin and heparan sulfate, is involved in a large number of biological activities and plays a crucial role in the maintenance, survival and selective vulnerability of various neuronal populations in the normal, injured, or diseased brain. An injury in the CNS may trigger FGF2 gene expression and promote reactive astrocytes and injured neurons to synthesize increased amounts of FGF2, which in turn protects injured neurons from death and stimulates neuronal plasticity and tissue repair. These known trophic functions of FGF2 indicate that its administration soon after a neuronal injury may prevent or mitigate the early stages of neuronal degeneration and contribute to the survival or slow the death of injured neurons. Cell soma atrophy, the condensation of nuclear chromatin, and subsequent DNA fragmentation are generally believed to indicate that an injured neuron is undergoing apoptotic cell death. Neurons undergoing apoptosis also can be distinguished by the activation of cysteine proteases, commonly known as caspases. Typically, these proteases exist as inactive pro-caspases in healthy cells, but under various pathological conditions, procaspases are cleaved, and the resulting active caspases trigger a cascade of events that leads to apoptotic cell death. Thus, caspase activation is thought to play a central role in apoptosis. In the caspase family, caspase-3 is one of the major members implicated in neurons undergoing apoptotic cell death. Currently, caspase-3 activation has been observed in neurons after various forms of injury and is considered to be a key mediator of apoptosis. We investigated caspase-3 activity in axotomized dLGN projection neurons immediately following injury using an antibody raised against fractin, a 32 kDa N-terminal actin fragment that results exclusively from the cleavage of beta actin by activated caspase-3. Thus while other proteases such as calpain may be involved in the death of axotomized dLGN neurons, the presence of fractin confirms the involvement of caspase-3. The present results demonstrate that the majority of axotomized dLGN projection neurons undergo apoptotic cell death, and they provide details about the initiation, duration, and cytological distribution of activated caspase-3 activity in injured dLGN projection neurons. All BDA-labeled neurons were examined with a brightfield microscope at a magnification of 1000X. Since the BDA labeling quality varied significantly among individual dLGN projection neurons, structural analysis was restricted to projection neurons that appeared to be completely labeled. Using the same criteria as described previously, the cell soma and dendrites of a neuron considered to be completely labeled  with BDA and contained within a single 75 mm Albaspidin-AA section on a clean background without interference from other labeled neuronal profiles were analyzed. Observing these constraints stringently, completely labeled projection neurons in the dLGN were traced with the aid of a camera lucida drawing tube attachment.
with BDA and contained within a single 75 mm Albaspidin-AA section on a clean background without interference from other labeled neuronal profiles were analyzed. Observing these constraints stringently, completely labeled projection neurons in the dLGN were traced with the aid of a camera lucida drawing tube attachment.