Because the system is used widely, a number of strategies for enhancing protein production have been developed. However, most strategies do not target the protein itself, but instead modify other aspects of the process, such as the host, promoter, signal peptide, chaperone, fusion proteins, protease, fermentation conditions, codon optimization, or gene copy number. Although these methods can effectively enhance the Forsythin expression of some proteins, it is challenging to enhance the secretion of certain proteins that are retained in the cell. Previous studies have shown that the rational design of the internal regions of a protein can enhance its secretion by P. pastoris. Therefore, some secretion signals that affect protein secretion must exist in the internal regions of proteins. It may therefore be necessary to modify the sequence or structure of a protein to enhance its secretion. In this study, we used methyl parathion hydrolase from Ochrobactrum sp. M231 to investigate the effect of modification of its N-terminus on secretion. Organophosphorus hydrolases play important roles in the decontamination and bioremediation of environments polluted by organophosphate pesticides. MPH, isolated by our lab from Ochrobactrum sp. M231 in 2008, can efficiently and specifically Evodiamine degrade methyl parathion, but it cannot be secreted from P. pastoris. However, another OPH, OPHC2, isolated from Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes, also by our laboratory, has a similar three-dimensional structure to MPH. It has been over-expressed and efficiently secreted at concentrations of up to 5.5 g/L in P. pastoris. These two proteins have the same function and share a sequence identity of 47.7%. However, they have different secretion pa erns when expressed in the same P. pastoris expression system with an identical promoter and signal peptide. Although it has been reported that integrating 12 copies of the MPH expression casse e into the P. pastoris system can significantly improve the secretion of MPH and that MPH can be expressed and secreted by Bacillus subtilis WB800, secretion levels with these two methods are still close to 100-fold lower than the levels of OPHC2 secreted by P. pastoris. We a empted to identify the protein sequence factor that affected the secretion of MPH by P. pastoris. Sequence and structural analyses revealed that MPH and OPHC2 have different Nterminal regions. Therefore, the aim of this study was to improve the secretion of MPH by P. pastoris through the modification of its N-terminal structure. In this study, MPH from  Ochrobactrum sp. M231 was selected and the importance of its N-terminus in its secretion by P. pastoris was determined. We swapped the corresponding block of sequence from OPHC2 based the Schema software analysis and removed the N-terminal block of MPH according to the 3D protein structures. Our results revealed that the N-terminal region plays an important role in secretion. In addition, the improved secretion of the MPH mutants was not due to differences in growth rate, mRNA expression, gene copy number, or stability. Although the mutant proteins had reduced catalytic efficiency, the secretion of both D10-MPH and N9-MPH was improved significantly compared to wild-type MPH, as demonstrated by SDS-PAGE.
Ochrobactrum sp. M231 was selected and the importance of its N-terminus in its secretion by P. pastoris was determined. We swapped the corresponding block of sequence from OPHC2 based the Schema software analysis and removed the N-terminal block of MPH according to the 3D protein structures. Our results revealed that the N-terminal region plays an important role in secretion. In addition, the improved secretion of the MPH mutants was not due to differences in growth rate, mRNA expression, gene copy number, or stability. Although the mutant proteins had reduced catalytic efficiency, the secretion of both D10-MPH and N9-MPH was improved significantly compared to wild-type MPH, as demonstrated by SDS-PAGE.
In CRC is mostly limited by observational population-based or clinic-based retrospective studies
No definitive conclusions on the effects of Gentiopicrin metformin for CRC can be drawn at the molecular level. Up till now, the prognostic significance for diabetic patients with CRC using metformin in survival outcomes has not been systematically assessed. And recent meta-analysis only investigated the general cancer outcomes and all-cause mortality. However, as a systemic disease which can involve different organs to various extent, diabetes can show variation between different cancer types on prognostic effects. Therefore, we performed a systemic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the effect of metformin on survival outcomes in diabetic patients with CRC. As the two most common diseases worldwide, diabetes and colorectal cancer share many risk factors. Previous metaanalyses have demonstrated that type 2 diabetes is associated with increased risk of CRC and metformin is a commonly prescribed anti-diabetic agent in outpatients. We sought to comprehensively investigate the relationship between metformin exposure and CRC outcomes in patients with diabetes by pooling survival data from all studies. In fact, our meta-analysis including 23,255 participants from six cohort studies revealed that diabetic patients with CRC taking metformin achieved an estimated OS benefit of 44% compared with non-metformin users. The potential antitumor effect for metformin has not been fully elucidated, although several observational studies have reported such a trend. Metformin mediates mammalian target of rapamycin pathway via the activation of AMPK and tuberous sclerosis complex 2, phosphorylation of TSC2 which leads to an inhibition of mTOR signaling and reduction in protein synthesis for cancer cells. It also promotes p53-dependent autophagy and cell cycle arrest through a decrease in cyclin D1 protein level. Although experimental data indicate that metformin leads to mTOR inhibition, at present no mTOR inhibitors have been approved for the treatment of CRC patients. Our meta-analysis might be a consistent finding among different population cohorts even though potential confounding factors and risk of publication bias do exist. Though the observational studies cannot be 10-Gingerol interpretated as causation, several aspects can be taken into consideration recommended by Hill et al as evidence to support our conclusion. First, temporal association between metformin exposure and CRC incidence, which means CRC occurs after metformin exposure in all studies. Second, the results reveal a biological gradient or dose-response relationship in one study, with higher intensity metformin users exclusively having lower risk of CRC-specific mortality. Third, what we find is also biologically plausible as causality with the fact that metformin is found to reduce cancer cell proliferation, inhibit mTOR and protein synthesis and lead to cell cycle arrest. Fourth, consistent results are shown  in the forest plot for both individual study and pooled estimates of the six included studies. Fifth, significant strength of the association between metformin users and non users is revealed for an estimated OS benefit of over 40%. Several potential limitations to our meta-analysis need to be addressed. First, we did not fully investigate the heterogeneity of individual studies.
in the forest plot for both individual study and pooled estimates of the six included studies. Fifth, significant strength of the association between metformin users and non users is revealed for an estimated OS benefit of over 40%. Several potential limitations to our meta-analysis need to be addressed. First, we did not fully investigate the heterogeneity of individual studies.
In addition it provides a detailed high resolution reference for imaging techniques of cardiac
Second, follow-up data are lacking. In ischemic stroke, low IGF-I concentrations may predict poor outcome in humans. Further studies are needed to determine whether serum IGF-I levels predict outcomes after a stroke in our population. Furthermore, the biological effects and bioavailability of IGF-I are modulated through IGFBPs, which control IGF-I access to cell surface receptors. Unfortunately, we did not have IGFBPs; therefore, our results do not fully represent biologically active IGF-I. Finally, IGF-I measurements were done after the stroke and thus may not accurately reflect pre-stroke exposure. In conclusion, lower IGF-I levels are significantly related to risk of stroke, independent from other traditional and emerging risk factors, suggesting that they may play a role in the pathogenesis of AIS. Thus, IGF-I levels should be considered as a routine risk factor for stroke in the Chinese population, and further post-ischemic IGF-I therapy may be beneficial for stroke. We suggest routing screening of serum IGF-I levels to prevent stroke in the Chinese population. However, before a broad implementation of this recommendation, additional studies are needed for external validation. A network of extracellular matrix maintains the structural integrity of the myocardium. Due to several etiologies increased deposition of collagen and other extracellular matrix proteins can occur leading to Saikosaponin-B2 cardiac fibrosis. After myocardial infarction, cardiomyocytes are replaced by connective tissue leading to reparative fibrosis. In contrast, in nonischemic cardiomyopathies, an increase in collagen synthesis by myofibroblasts results in diffuse interstitial reactive fibrosis. In arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, fibrosis is accompanied by an increase of adipocytes leading to so-called fibrofa y replacement. Myocardial fibrosis is an important part of the histological characteristics in heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction and may act as a substrate  for cardiac arrhythmias. Adequate detection of the amount and distribution of fibrosis in the heart is important for diagnosis, predicting prognosis, treatment planning and follow-up after therapy. The reference noninvasive standard for indirect detection of myocardial fibrosis is late gadolinium enhancement on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Thus far, detailed histological correlation studies to validate this MRI technique are scarce. Histological assessment of cardiac fibrosis is mostly limited by the small amount of tissue available in diagnostic endomyocardial biopsies that only provides regional information. In addition, quantification of histological fibrosis is usually performed semiquantitatively, classifying the fibrosis in limited categories. The aim of this study was to determine the exact pa erns of fibrosis and fa y changes in the myocardium of patients with the PLN p.Arg14del mutation associated cardiomyopathy in relation to their clinical phenotype. This study population was used as proof-of-principle for a novel Procyanidin-B2 method of high resolution systematic digital quantification of fibrosis and fa y tissue in transversal cardiac slides. In the future this method may be used for detailed histological quantification and determination of the distribution paern of cardiac fibrosis in different types of heart disease.
for cardiac arrhythmias. Adequate detection of the amount and distribution of fibrosis in the heart is important for diagnosis, predicting prognosis, treatment planning and follow-up after therapy. The reference noninvasive standard for indirect detection of myocardial fibrosis is late gadolinium enhancement on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Thus far, detailed histological correlation studies to validate this MRI technique are scarce. Histological assessment of cardiac fibrosis is mostly limited by the small amount of tissue available in diagnostic endomyocardial biopsies that only provides regional information. In addition, quantification of histological fibrosis is usually performed semiquantitatively, classifying the fibrosis in limited categories. The aim of this study was to determine the exact pa erns of fibrosis and fa y changes in the myocardium of patients with the PLN p.Arg14del mutation associated cardiomyopathy in relation to their clinical phenotype. This study population was used as proof-of-principle for a novel Procyanidin-B2 method of high resolution systematic digital quantification of fibrosis and fa y tissue in transversal cardiac slides. In the future this method may be used for detailed histological quantification and determination of the distribution paern of cardiac fibrosis in different types of heart disease.
Arginine kinase has also been confirmed to be responsible for the antigenic cross-reactivity among arthropods
Although there were very few reports regarding whether a cross-reaction exists between silkworm moth and mites, intra- and interspecies cross-reactivities among allergens from mites and cockroaches have been widely recognized. A previous immunochemical study has reported cross-reactivity existing between house dust mites and snails, crustaceans, cockroaches, chironomids, and other mite allergens. In the majority of related studies, house dust mite extracts proved to be a powerful inhibitor for the cross-inhibition tests, suggesting that it is the main Isoacteoside source of many allergens resulting in  hypersensitivity. Our findings provide serum sIgE data showing that silkworm moth is an important allergen for respiratory allergies in the region and a positive correlation exists between silkworm moth and the relevant mites and cockroaches. We acknowledge that owing to the retrospective nature of the study, we cannot conclude on the cross-reaction between these allergens. Further serum inhibition studies are warranted to verify such relationship, and if so, it would be worthwhile to find out whether it is a ributed to arginine kinase. Features of Ursolic-acid diabetic retinopathy are retinal microaneurysms, retinal hemorrhages, retinal edema, retinal vein dilatation, and lipid deposition in the deep retinal layers. Since leakage of lipids, erythrocytes and serum through a vessel wall depends on the pressure in the vessel, since the diameter of a vessel also depends on its internal pressure, and since capillary blood pressure is influenced by the pressure in the draining veins, we assumed that an increased retinal vein pressure is a factor associated with presence and severity diabetic retinopathy. The blood pressure in the central retinal vein inside of the eye is at least as high as the orbital cerebrospinal fluid pressure, since the central retinal vein passes, after leaving the eye, through the optic nerve and the orbital cerebrospinal fluid space. We therefore put forward the hypothesis that an increased CSFP is associated with diabetic retinopathy. This hypothesis would fit with the role of arterial hypertension as risk factor for diabetic retinopathy, since a higher arterial blood pressure is associated with a higher CSFP. To test the hypothesis, we conducted a study in which we estimated the CSFP and compared eyes with diabetic retinopathy and eyes without diabetic retinopathy. In previous studies, the correlation between CSFP and age, arterial blood pressure and body mass index was described and a formula allowed estimating the CSFP. We used this formula to assess the CSFP in the participants of our study. We chose a population-based study design to avoid a referral induced bias in the selection of study participants. For all study participants, an interview was performed with standardized questions on the level of education, quality of life, known major systemic diseases, and other parameters. Fasting blood samples were taken for measurement of blood lipids, glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin HbA1c. Body height and weight and the circumference of the waist and hip were measured. The blood pressure was measured with the participant si ing for at least 5 minutes.
hypersensitivity. Our findings provide serum sIgE data showing that silkworm moth is an important allergen for respiratory allergies in the region and a positive correlation exists between silkworm moth and the relevant mites and cockroaches. We acknowledge that owing to the retrospective nature of the study, we cannot conclude on the cross-reaction between these allergens. Further serum inhibition studies are warranted to verify such relationship, and if so, it would be worthwhile to find out whether it is a ributed to arginine kinase. Features of Ursolic-acid diabetic retinopathy are retinal microaneurysms, retinal hemorrhages, retinal edema, retinal vein dilatation, and lipid deposition in the deep retinal layers. Since leakage of lipids, erythrocytes and serum through a vessel wall depends on the pressure in the vessel, since the diameter of a vessel also depends on its internal pressure, and since capillary blood pressure is influenced by the pressure in the draining veins, we assumed that an increased retinal vein pressure is a factor associated with presence and severity diabetic retinopathy. The blood pressure in the central retinal vein inside of the eye is at least as high as the orbital cerebrospinal fluid pressure, since the central retinal vein passes, after leaving the eye, through the optic nerve and the orbital cerebrospinal fluid space. We therefore put forward the hypothesis that an increased CSFP is associated with diabetic retinopathy. This hypothesis would fit with the role of arterial hypertension as risk factor for diabetic retinopathy, since a higher arterial blood pressure is associated with a higher CSFP. To test the hypothesis, we conducted a study in which we estimated the CSFP and compared eyes with diabetic retinopathy and eyes without diabetic retinopathy. In previous studies, the correlation between CSFP and age, arterial blood pressure and body mass index was described and a formula allowed estimating the CSFP. We used this formula to assess the CSFP in the participants of our study. We chose a population-based study design to avoid a referral induced bias in the selection of study participants. For all study participants, an interview was performed with standardized questions on the level of education, quality of life, known major systemic diseases, and other parameters. Fasting blood samples were taken for measurement of blood lipids, glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin HbA1c. Body height and weight and the circumference of the waist and hip were measured. The blood pressure was measured with the participant si ing for at least 5 minutes.
Diffusion is severely impaired by fibrosis of the alveolar matrix or by inflammatory cell infiltration
On respiratory function testing, the degree of gas transfer reduction is reflected by the decrease in the diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide, which is also reduced in DM-IP. However, in patients with severe DM-A/SIP, accurate pulmonary function testing is impossible due to complications such as dyspnea and pneumomediastinum. Therefore, the PO2 is simple and prognostically useful. In the DM-A/SIP patients treated by early CSA/PDN combination therapy, ferritin $600 ng/ml and PO2 $45 Torr were independent prognostic factors, and all patients with both of these factors died. In these patients, the outcome could not be improved even by additional treatments such as IVCY and IVIG. Recently, mycophenolate mofetil and blood purification therapy have been reported to be effective in patients with refractory DM-A/SIP. In patients with a poor prognosis, immunosuppressant therapy such as IVCY and mycophenolate mofetil and blood purification therapy should be considered from the beginning of treatment in addition to early CSA/PDN combination therapy. The clinical course of DM-A/SIP is rapidly progressive and this biomarker may not reflect the disease activity in rapid course of interstitial pneumonia. This study was carried out retrospectively in a small number of patients. In addition, autoantibodies and lung high-resolution computed tomography findings were not evaluated in all enrolled patients or in a large number of patients. Prognostic factors associated with the disease must still be extracted by evaluating a larger number of patients. In mammalian organisms, Campesterol steroid hormones are indispensable for a normal development. Considering their action, these steroids are classified into three main groups. Mineralocorticoids, with aldosterone as the most important representative, regulate the salt household and hence the blood pressure. Cortisol belongs to the glucocorticoids and provides the organism with energy stimulating the gluconeogenesis. Finally, the sexual hormones, with androgens and estrogens, are fundamental for the 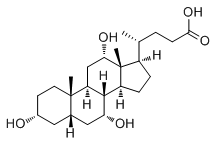 formation of the sexual characteristics and the estrous cycle. Biosynthesis of all steroid hormones is initiated by CYP11A1 with the side chain cleavage of cholesterol yielding pregnenolone. This ratelimiting step of the steroid hormone biosynthesis is carried out in the inner mitochondrial membrane and displays three hydroxylation reactions. In the first step, carbon C22 of cholesterol is hydroxylated followed by an oxidative attack at C20, forming the intermediate 20,22-dihdroxycholesterol. The cleavage of the side chain of cholesterol is initiated by a third hydroxylation. The electrons necessary oxygen activation and substrate hydroxylation are transferred from NADH via a NADH-depending 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C ferredoxin reductase, adrenodoxin reductase, and a ferredoxin, adrenodoxin. The product pregnenolone serves as precursor for mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, as well as DHEA and its derived sexual hormones. To induce their biological activities, according to recent hypothesis steroid hormones have to be available in an unconjugated form to interact with their corresponding receptors. Conjugated steroids with sulfate groups have been regarded for a long time to be exclusively designated for excretion.
formation of the sexual characteristics and the estrous cycle. Biosynthesis of all steroid hormones is initiated by CYP11A1 with the side chain cleavage of cholesterol yielding pregnenolone. This ratelimiting step of the steroid hormone biosynthesis is carried out in the inner mitochondrial membrane and displays three hydroxylation reactions. In the first step, carbon C22 of cholesterol is hydroxylated followed by an oxidative attack at C20, forming the intermediate 20,22-dihdroxycholesterol. The cleavage of the side chain of cholesterol is initiated by a third hydroxylation. The electrons necessary oxygen activation and substrate hydroxylation are transferred from NADH via a NADH-depending 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C ferredoxin reductase, adrenodoxin reductase, and a ferredoxin, adrenodoxin. The product pregnenolone serves as precursor for mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, as well as DHEA and its derived sexual hormones. To induce their biological activities, according to recent hypothesis steroid hormones have to be available in an unconjugated form to interact with their corresponding receptors. Conjugated steroids with sulfate groups have been regarded for a long time to be exclusively designated for excretion.